Just as we thought the artificial intelligence (AI) model arena was settling down a little, Anthropic has launched Claude 3 which is capable of outperforming ChatGPT in a number of areas. Claude 3 is available in three distinct models: Haiku, Sonnet, and Opus, each offering its own unique capabilities. Opus is the most powerful and capable, designed for complex logic and intense prompts, while Haiku is the fastest but less accurate, intended for instant customer service responses. Sonnet is a free, intermediate model available to the public. Although all are now being tested against ChatGPT and Google Gemini 1.0 Ultra, with Claude 3 Opus outperforming both in various benchmarks.
Let’s dive into the details. Anthropic has three models as each has its own strengths. Haiku is the speedster, designed for quick replies, perfect for customer service. Sonnet is the middle child, offering a good mix of speed and smarts, and it’s free for you to use, although there’s a limit on how much you can use it each day. Then there’s Opus. Opus is the star of the show, the one you’d want on your team for the toughest challenges. It’s not free, costing $20 a month, but for that price, you get the best logic and problem-solving abilities out there.
Now, let’s talk about a feature that’s really exciting: vision capabilities. Opus can now understand pictures. This is a big deal because it opens up so many possibilities. Think about it: you could show it a design, and it could give you feedback, or you could ask it to describe what’s happening in a photo. This is a huge step forward for AI.
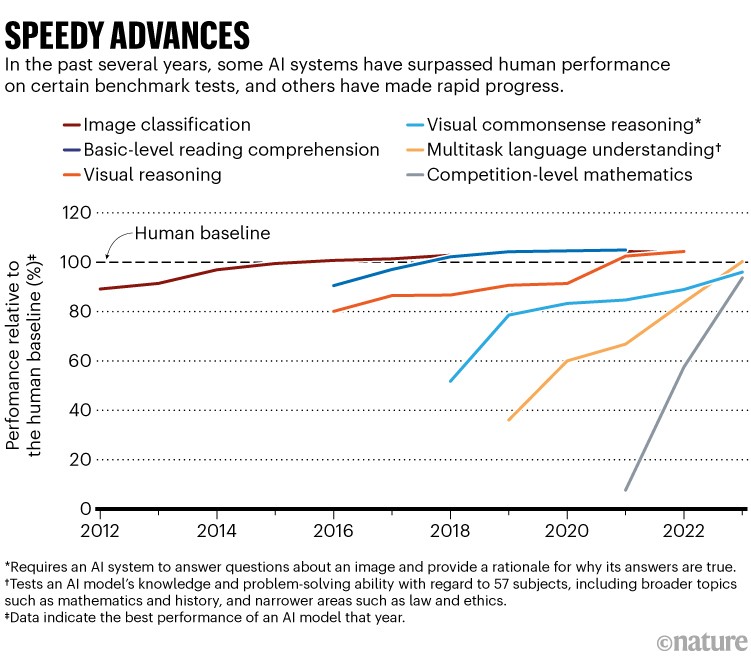
Claude 3 results beat ChatGPT
But it’s not just about being smart and fast. Anthropic has worked hard to make sure these AIs are user-friendly and less biased. This is important because it means more people can use them without running into unfair or prejudiced responses. Making AI accessible and fair is a big challenge, but it’s one that Anthropic is tackling head-on.
To really understand how good these AIs are, Anthropic didn’t just use standard tests. They made their own benchmarks. This means they could really focus on what each AI model is best at and make sure they’re up to the task, no matter what industry they’re used in. Watch the overview video below created by Matt Wolfe to learn more about the differences between the three different Claude AI models now available and how their results compare to OpenAI’s ChatGPT.
Here are some other articles you may find of interest on the subject of Claude 3
The differences between Claude 3 AI models
The Claude 3 model family introduces a significant advancement in the domain of artificial intelligence, comprising three distinct models named Haiku, Sonnet, and Opus, each designed to cater to varying demands of speed, intelligence, and application scope. This family of models represents a new benchmark in AI capabilities, offering enhanced performance across a broad spectrum of cognitive tasks. Here’s an overview of each:
Haiku
Haiku is the entry-level model within the Claude 3 family, characterized by its unparalleled speed and cost-effectiveness. It’s designed for applications requiring near-instantaneous responses, making it ideal for tasks like customer interactions, content moderation, and efficient management of logistics and inventory. Despite its rapid response rate, Haiku doesn’t compromise on intelligence, providing smart and accurate support in live interactions, translations, and knowledge extraction from unstructured data. With a context window of 200K tokens and a pricing model designed to be highly affordable, Haiku aims to be the fastest and most cost-efficient option in its intelligence category, catering to use cases that demand swift, reliable AI processing.
Sonnet
Sonnet occupies the middle ground in the Claude 3 model family, offering a balanced mix of intelligence and speed. It is twice as fast as its predecessors (Claude 2 and Claude 2.1) and is designed to support a wide range of enterprise workloads at a lower cost. Sonnet excels in rapid knowledge retrieval, sales automation, data processing, and code generation. Its robust performance makes it suitable for tasks like product recommendations, forecasting, targeted marketing, and quality control. Like Haiku, Sonnet offers a 200K context window but brings enhanced endurance and affordability for large-scale AI deployments, making it an ideal choice for businesses seeking a potent combination of speed, intelligence, and cost-efficiency.
Opus
Opus represents the pinnacle of the Claude 3 model family, offering the highest level of intelligence among the trio. It outperforms other models in the market on complex cognitive tasks, showcasing near-human levels of comprehension and fluency. Opus is capable of navigating open-ended prompts and unseen scenarios with remarkable adeptness, making it suitable for advanced applications like task automation across APIs and databases, R&D, and strategic analysis. Although it delivers similar speeds to Claude 2 and 2.1, its superior intelligence enables it to process complex information and perform highly sophisticated tasks. With a 200K context window, expandable to 1 million tokens for specific cases, Opus is tailored for users requiring the utmost in AI capability.
Cross-Model Features and Innovations
All three models in the Claude 3 family demonstrate significant improvements in vision capabilities, processing a wide range of visual formats and reducing unnecessary refusals by showing a more nuanced understanding of requests. They exhibit enhanced accuracy in responses, with Opus, in particular, showing a remarkable improvement in providing correct answers for challenging questions. The Claude 3 models have been designed with long contexts and near-perfect recall abilities, supporting inputs exceeding 1 million tokens for specific applications.
A key focus has been placed on responsible design, with dedicated teams working to mitigate risks associated with misinformation, CSAM, and other potential harms. Efforts to address biases and promote neutrality have also been advanced, with the Claude 3 models demonstrating reduced biases compared to previous iterations.
In terms of usability, these models have been refined to better follow complex, multi-step instructions and to adhere to brand voice and response guidelines, simplifying the creation of trustworthy customer-facing experiences. The models also support structured output formats like JSON, enhancing their applicability across various natural language processing tasks.
So, what does all this mean for you? If you’re someone who’s interested in AI, whether you’re a developer, a business owner, or just curious, Claude 3’s models are worth paying attention to. They’re not just another set of AIs; they’re a step up in what artificial intelligence can do. With their ability to handle complex tasks, understand images, and do it all with less bias, they’re setting a new standard. And with options for different needs and budgets, there’s a good chance one of these models could be just what you’re looking for.
The Claude 3 model family represents a significant leap forward in the field of AI, offering users a spectrum of choices to meet their specific needs, from the ultra-fast and cost-effective Haiku to the balanced Sonnet, and the highly intelligent Opus. With advancements in speed, accuracy, vision capabilities, and a commitment to responsible AI development, the Claude 3 models set new industry standards and offer promising solutions for a wide range of applications.
Filed Under: Guides, Top News
Latest timeswonderful Deals
Disclosure: Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, timeswonderful may earn an affiliate commission. Learn about our Disclosure Policy.