The fusion of robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) to create humanoid robots represents a frontier of innovation that captivates both the imagination and the intellect. This fascinating interplay of disciplines aims to craft machines that not only mimic human appearance but also exhibit an unprecedented level of autonomy and intelligence. You’ll be pleased to know that this article delves into the core aspects of this subject, offering an insightful exploration suitable for both enthusiasts and professionals.
These fields are not just changing the way we think about machines, but they are also reshaping our daily lives and work environments. One of the most talked-about developments in this area is Tesla’s humanoid robot, Optimus. This robot, which has been designed to handle routine tasks, has recently shown off its improved ability to walk.
Elon Musk, the CEO of Tesla, has a vision where robots like Optimus will take over the repetitive tasks that humans currently do, freeing us up for more creative endeavors. The latest version of this robot, known as Optimus Gen 2, has demonstrated new features that suggest robots are becoming more independent and capable.
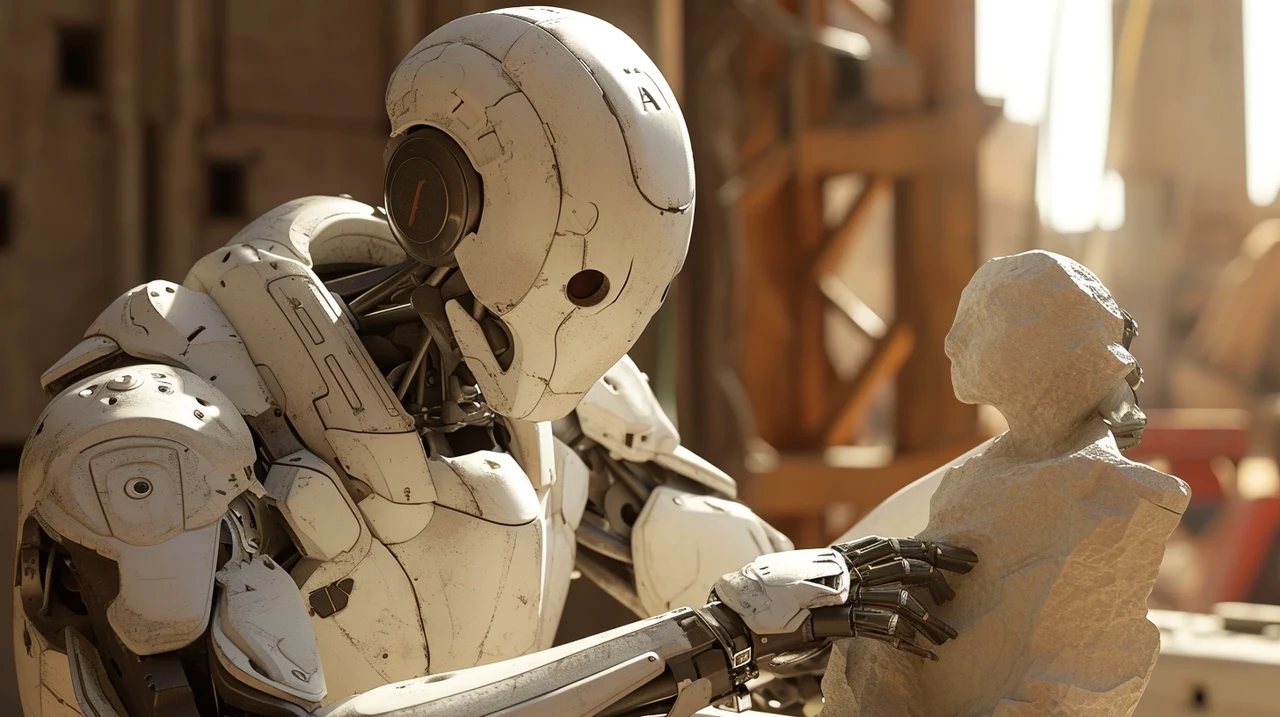
Figure AI humanoid robot
For those who follow the business aspects of technology, there’s an exciting development involving a robotics startup called Figure AI. This company is currently in talks to secure a large amount of funding, with tech giants Microsoft and OpenAI showing interest. If successful, this deal could increase Figure AI’s value to $2 billion.
Although the deal isn’t finalized, Figure AI has already started working with BMW. They are planning to bring autonomous humanoid robots into the car manufacturing process, which could revolutionize the way cars are made by automating complex tasks and making production more efficient. In the demonstration video below you can see the Figure AI humanoid robot making a coffee.
Advancements in Robotics and Artificial Intelligence
Meanwhile, in the field of AI research, NVIDIA is making significant strides. Dr. Jim Fan, a senior research scientist at NVIDIA, is working on creating what’s known as a ‘foundation agent.’ This is a type of AI that can learn in simulated environments and then apply what it has learned to real-world situations. NVIDIA’s projects, Isaac Gym and Isaac Sim, are central to this research. They suggest a future where robots can easily adjust to different tasks and environments, making them incredibly versatile.
Here are some other articles you may find of interest on the subject of humanoid robots and robotics :
Tesla’s work with Optimus is a clear example of how robotics and AI are coming together to create a future where robots assist us with a wide range of tasks, from the mundane to the complex. The improvements seen in Optimus Gen 2 indicate that the day when robots will be a common presence in our lives is getting closer. These robots are set to become our assistants, helping us with everyday tasks and making our lives easier.
The potential investment in Figure AI, along with its partnership with BMW, shows that there is a significant commercial interest in robotics. Introducing autonomous humanoid robots into manufacturing has the potential to completely change the industry. It could make production lines more efficient and safer by reducing the need for humans to perform dangerous or monotonous tasks.
Building AI Humanoid Robots
NVIDIA’s research, under the guidance of Dr. Fan, is pushing the boundaries of what AI agents can do. By training these agents in virtual environments, they are laying the groundwork for AI that can transition smoothly from simulations to real-world applications. This research could lead to the development of robots that are not only autonomous but also adaptable, able to take on a variety of roles and adjust to different settings.
- Robotics: The physical embodiment of the robot, including its mechanical design, sensors, actuators, and control systems.
- Artificial Intelligence: The brain of the robot, encompassing machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, and computer vision, allowing the robot to perceive, understand, and act in its environment.
The Synergy of Robotics and AI
Combining robotics and AI is not merely about assembling parts; it’s about creating an entity that learns and adapts. Here’s how these technologies synergize:
- Perception and Understanding: AI enables robots to interpret sensory information, making sense of their surroundings and identifying objects and people.
- Decision-making: AI algorithms process data to make autonomous decisions, guiding the robot’s actions in real-time.
- Learning and Adaptation: Through machine learning, robots can improve their performance based on experience, becoming more efficient and versatile over time.
Real-world Applications
Humanoid robots, equipped with AI, are not just a staple of science fiction; they’re increasingly becoming part of our reality. Some of the domains they are impacting include:
- Healthcare: Assisting with patient care and performing repetitive tasks, freeing human staff for more complex duties.
- Customer Service: Handling inquiries and providing assistance in banks, airports, and retail environments.
- Education: Supporting teachers with administrative tasks and offering personalized learning experiences.
Challenges and Considerations
While the prospects are exciting, combining robotics and AI to create humanoid robots presents its own set of challenges:
- Technical Complexity: Designing systems that can reliably interpret and interact with the unpredictable nature of the human environment is immensely challenging.
- Ethical and Social Implications: Issues such as privacy, employment displacement, and the ethical treatment of AI entities are crucial considerations for developers and society.
In case you’re curious how these technological humanoids might affect your life, it’s worth noting that the aim is to augment human capabilities and improve quality of life. From performing hazardous tasks to providing companionship, humanoid robots have the potential to significantly impact various aspects of our daily lives.
The Future of AI humanoid Robotics
As we continue to explore the potential of humanoid robots, the journey is as much about enhancing their physical capabilities as it is about imbuing them with ethical and social understanding. The integration of robotics and AI stands as a testament to human ingenuity, promising a future where technology and humanity coexist in harmony.
The advancements made by Tesla with Optimus, the potential funding for Figure AI, and NVIDIA’s groundbreaking research are all significant steps forward in the fields of robotics and AI. These developments are pointing us toward a future where robots are an integral part of our daily lives, offering solutions to some of the most tedious and complex problems we face. As these technologies continue to progress, they promise to transform industries and improve our overall quality of life. With each new breakthrough, we get a glimpse of a future where the partnership between humans and robots becomes ever more seamless and beneficial.
At its core, the creation of humanoid robots involves intricate engineering and sophisticated AI algorithms. These robots are designed to perform tasks ranging from simple domestic chores to complex interactions in social and industrial settings. To enhance your experience of understanding this complex integration, it’s essential to grasp the primary components involved:
The journey of combining robotics and AI to create humanoid robots is a complex but thrilling endeavor that reflects the pinnacle of technological innovation. With each advancement, we edge closer to a future where these robotic counterparts not only exist among us but also contribute significantly to society. As this field continues to evolve, it promises to unveil new horizons for human achievement and interaction.
Filed Under: Guides, Top News
Latest timeswonderful Deals
Disclosure: Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, timeswonderful may earn an affiliate commission. Learn about our Disclosure Policy.