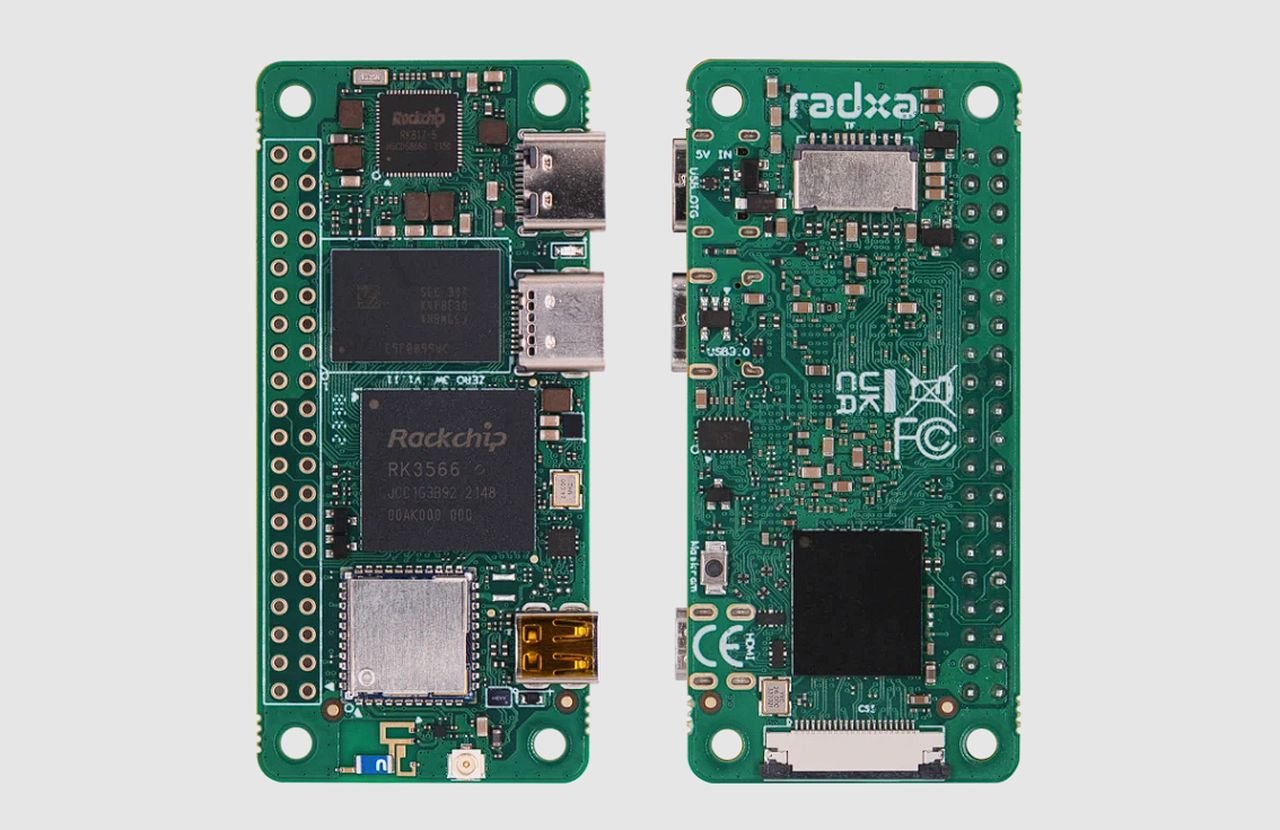
Offering an alternative to the smaller Raspberry Pi mini PCs the Radxa Zero 3W, a small but mighty single board computer equipped with robust features and attractive price point. This tiny powerhouse is designed to cater to the needs of both hobbyists and professionals, offering a versatile platform for a wide range of projects. Starting at just $19 and going up to $68, depending on the configuration, it’s an affordable option for those looking to dive into the world of computing without breaking the bank.
At the heart of the Radxa Zero 3W lies the Rockchip RK 3566 SoC, which works in tandem with a quad-core ARM Cortex-A55 processor. This combination delivers a performance that strikes a perfect balance between power consumption and efficiency, making it suitable for a variety of uses. Whether you’re setting up a media center, creating digital signage, or working on a different project that requires visual output, the Mali G52 2E GPU ensures that the Radxa Zero 3W can handle the task with ease.
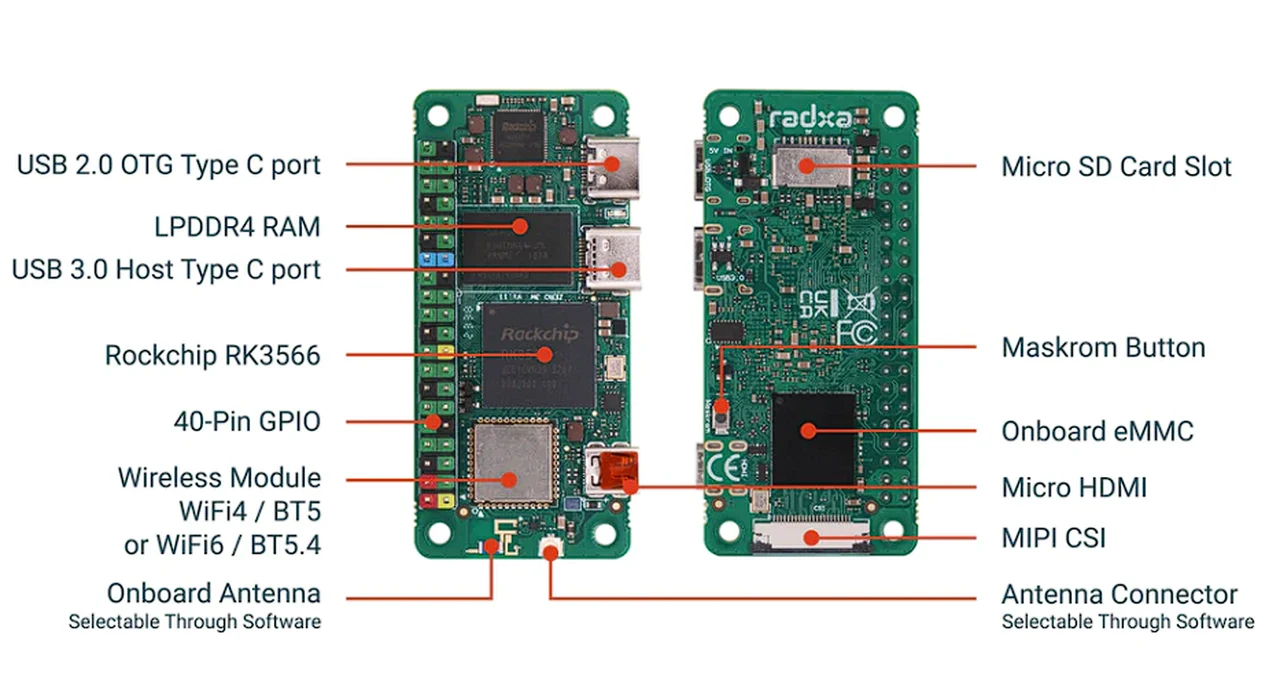
The inclusion of DDR4 RAM means that multitasking is smoother than ever, allowing users to run multiple applications without a hitch. Connectivity is another strong suit of this SBC, as it supports the latest Wi-Fi 6 and Bluetooth 5.4 standards. This means faster and more reliable wireless connections, which are essential in today’s interconnected world. The Radxa Zero 3W doesn’t skimp on physical connections either, offering USB-C ports, a micro HDMI connector, and a 40-pin GPIO header to meet various expansion needs.
Radxa Zero 3W single board computer (SBC)
Here are some other articles you may find of interest on the subject of alternatives to the Raspberry Pi range of mini PCs :
When it comes to storage, the Radxa Zero 3W provides users with options. You can choose between onboard eMMC flash storage for faster data transfer rates or a micro SD card slot for added flexibility. The eMMC option is particularly advantageous for those who prioritize quick operating system and application loading times. Additionally, a CSI camera serial interface connector is available for those interested in image or video capture projects.
Out of the box, the Radxa Zero 3W is ready to go with Debian Bullseye and an XFCE desktop environment, providing a stable and user-friendly platform. For those who prefer a different flavor of Linux, the SBC also supports Ubuntu, among other distributions, allowing users to tailor their experience to their specific project requirements.
However, it’s not all smooth sailing. Users looking to install an operating system on the eMMC flash storage may face a challenge due to the absence of a bootloader file. This means that some extra steps are necessary to get the system up and running. But once you’ve navigated this hurdle, the performance benefits of the eMMC storage are clear, with faster boot times and more responsive applications, which can be crucial for projects where time is of the essence.
Raspberry Pi alternative
When placed side by side with other zero form factor SBCs like the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W and the Orange Pi Zero 2W, the Radxa Zero 3W holds its own. It offers competitive features and performance, with advanced wireless capabilities and quicker storage options that make it a formidable player in the SBC market.
The Radxa Zero 3W is a compelling choice for a wide array of applications, thanks to its solid specifications and support for popular Linux distributions. As the community continues to explore and utilize this board, we can expect to see a wealth of insights into its true potential and the innovative projects it enables. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a curious hobbyist, the Radxa Zero 3W is a small computer that’s worth keeping an eye on. For more details on pricing, availability and full specifications jump over to the official Radxa website.
Filed Under: Hardware, Top News
Latest timeswonderful Deals
Disclosure: Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, timeswonderful may earn an affiliate commission. Learn about our Disclosure Policy.