[ad_1]
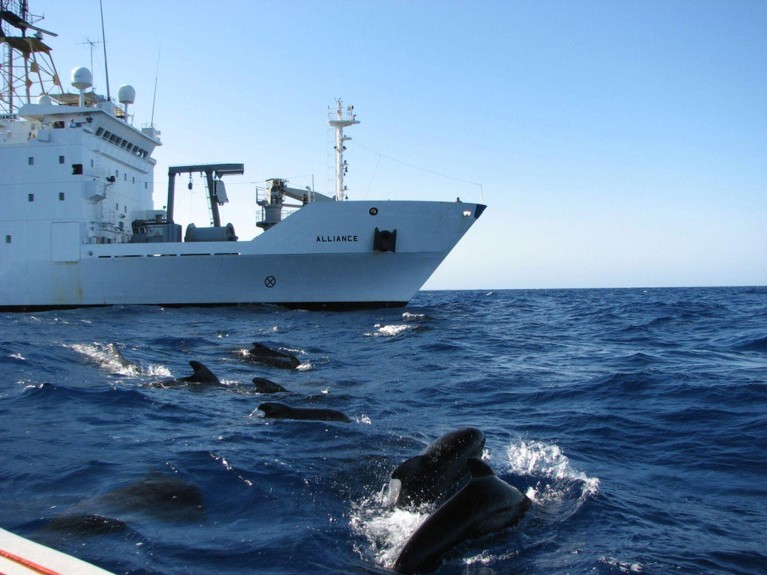

A NATO research vessel conducting studies of marine mammals in the Mediterranean Sea (pictured in 2009).Credit: U.S. Navy Petty Officer 2nd Class Kristen Allen via Mil image/Alamy
Science has been essential to the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), the political and military alliance founded 75 years ago this month. The 32-country alliance is admitting more members as it faces evolving geopolitical and military threats. The organization’s scientific work focuses largely on defence and civil-security projects that, for instance, investigate how climate change is affecting war, how emerging technologies could enhance soldiers’ performance and how to reduce discrimination and intolerance among military personnel. “The role of science and technology for NATO is likely to grow significantly over the next two decades,” predicts Simona Soare, a defence-technologies researcher at Lancaster University, UK.
How does NATO use science?
“We’re looking to make sure that we can provide scientific advice to the nations of NATO to enable them to maintain a technical and military advantage,” says Bryan Wells, a chemist and the organization’s chief scientist. Wells works at NATO’s Brussels headquarters, where world leaders gathered earlier this month to mark the organization’s 75th anniversary.
NATO has a complex organizational structure including both military and civilian staff. The civilian part of NATO is headed by a senior political figure from a member state and also includes diplomats representing member countries. The military part is headed by senior military personnel.
Much of NATO’s research and development (R&D) takes place through the Science and Technology Organization (STO), a network of more than 6,000 scientists at universities and national laboratories and in industry. They work together on defence research projects. NATO’s member states and non-member countries together contribute around €350 million (US$380 million) annually for the work of this network, says Wells.
The STO also has its own research laboratory, the Centre for Maritime Research and Experimentation (CMRE) in La Spezia, Italy. The laboratory employs around 150 people and is led by Eric Pouliquen, a physicist who has worked on underwater remote sensing.
NATO’s civilian arm provides grants for a Science for Peace and Security (SPS) research programme, headed by Claudio Palestini, a researcher in communications engineering.
The programme funds studies in areas such as counterterrorism and cyber defence. Earlier this month, the SPS programme updated its priorities. These now include studies on the impact on defence and security from climate change and from AI; protecting underwater infrastructure, and what it calls “hybrid threats”, which includes interference in elections and disinformation. Each of its larger grants is worth between €250,000 and €400,000 and lasts for two to three years.
Wells says the STO publishes research — mostly from the CMRE — in peer-reviewed journals where possible. “We recognize if we can publish openly, it’s very beneficial to do that,” he says.
However, many of its research projects are classified. NATO also does not publish a detailed breakdown of its R&D income and expenditure by country; nor does it release its funding trend data.
What sort of research is NATO doing?
Projects cover a spectrum of fields including using autonomous undersea surveillance to hunt for and identify mines; tracking and identifying submarines; quantum radar; and synthetic biology.
For example, one programme led by CMRE researchers explores how autonomous underwater vehicles can identify submarines using quantum technologies and artificial intelligence. Similarly, another project, ‘Military Diversity in Multinational Defence Environments: From Ethnic Intolerance to Inclusion’ studied the reasons for intolerance within NATO members’ armed forces as part of an overall strategy to improve diversity and inclusion across the organization..
NATO is examining how AI could affect troops’ ability to conceal themselves and evade detection. Another initiative is investigating how biotechnology could boost soldiers’ performance by enhancing the microbiome or through brain-computer interface technologies.
Why is NATO interested in climate research?
NATO is concerned that climate change has significant impacts on security. Melting sea ice creates more routes for naval shipping in the Arctic, for example, and NATO and non-NATO countries are increasingly operating in the region.
NATO is also interested in how temperature changes could affect the security of its member and non-member countries as well as of military installations around the world. In a 2024 review paper in the Texas National Security Review, CMRE researchers — along with colleagues from the University of St Andrews, UK, the University of L’Aquila, Italy, and the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich — found that submarines could become more difficult to detect using sonar in the North Atlantic Ocean as water temperature rises.
In another study, presented at last week’s conference of the European Geosciences Union in Vienna , CMRE researchers working with scientists at the universities of Princeton in New Jersey and Central Florida in Orlando assessed how extreme weather might affect 91 NATO military bases and installations. The researchers found that multiple bases and installations are likely to become susceptible to climate change as emissions continue to rise.
In another project, last year one of NATO’s research vessels moored vertical lines holding oceanographic and acoustic recorders in the Arctic Ocean. The intention was to monitor temperature, salinity and ambient noise throughout the water column. Other research projects are looking at the use of new materials for military clothing in warmer climates, says Wells.
In 2022, NATO also published the first of a series called Climate change and Security Impact Assessment. It is also developing a methodology to map greenhouse-gas emissions from NATO-member military activities and installations.
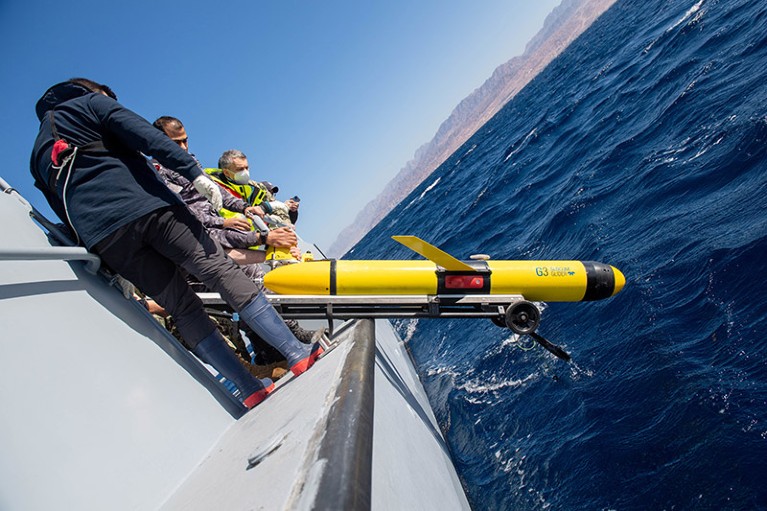

Personnel from NATO and the Royal Jordanian Navy lower an unmanned undersea vehicle into the Gulf of Aqaba (pictured in 2022).Credit: U.S. Navy photo by Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Dawson Roth
How has NATO’s expansion affected science?
NATO’s membership has more than doubled since its founding on 4 April 1949. Finland and Sweden are the latest countries to join. Three more — Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia and Ukraine — want to become members.
More members potentially means more funding and support for research and development, as well as access to a bigger pool of scientific expertise. However, Finland and Sweden both participated in NATO’s collaborative research for several years before they joined, says Wells.
Soare says that NATO’s defence science originally focused on aerospace, to help its members catch up after the Soviet Union launched Earth’s first artificial satellites — Sputnik 1 and Sputnik 2 — in 1957. “Throughout the cold war, ensuring air superiority was considered crucial,” she says.
What about a role for science in diplomacy?
In 1958, NATO established research fellowships and projects in what later became its Science for Peace and Security programme, to boost collaboration between nations including the United States and the Soviet Union. “Science provided a path for superpower adversaries to cooperate,” says Paul Arthur Berkman, founder of the Science Diplomacy Center in Falmouth, Massachusetts.
The fellowships and collaborative projects continued to provide a point of contact between NATO and Russia until 2014, when Russia invaded Crimea. That year, Russia, Romania and the United States were jointly developing a system to connect telemedicine capabilities across all three countries to provide medical care in remote and emergency situations. However, the invasion prompted NATO to freeze cooperation with Russia.
Berkman, who in 2010 co-organized and chaired the first dialogue between NATO and Russia regarding environmental security in the Arctic, is concerned at the alliance’s shift away from using science as a “safety valve” in its relations with Russia. He warns that cutting off scientific dialogue with Russia undermines democracy and nations’ ability to tackle global challenges such as climate change.
“Open science is akin to freedom of speech. If we turn off open science, in a sense we’re undermining democracy,” says Berkman.
[ad_2]
Source Article Link