[ad_1]
Hello Nature readers, would you like to get this Briefing in your inbox free every day? Sign up here.
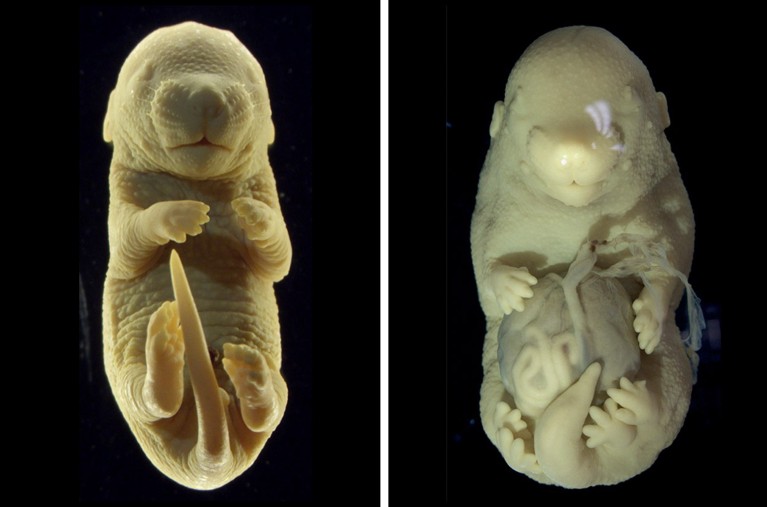
A typical mouse embryo (left) has four limbs. An embryo in which a particular gene was switched off halfway through development has six limbs, and several of its internal organs protrude from its abdomen.Credit: Anastasiia Lozovska et al/Nat. Comms
Developmental biologist Moisés Mallo and his colleagues inactivated a gene in a mouse embryo to see how the change affected spinal-cord development. One of the bioengineered embryos developed genitals that looked similar to two extra hind limbs. The finding led the researchers to unexpected discoveries about which changes in DNA’s 3D structure affect how embryos develop. “I didn’t choose the project, the project chose me,” Mallo says.
South Korea will become the first East Asian country to join the European Union’s €95-billion (US$102-billion) Horizon Europe research-funding programme. The country’s researchers will be eligible to apply for grants from a €53.5 billion pot of funding for research into global challenges in health, energy, climate change and industrial competitiveness. Last year, New Zealand became the first country to ‘associate to’ Horizon Europe, Canada will be signing on later this year, and Singapore and Japan are in preliminary discussions with the European Commission.
Studies in mice reveal that when long-term memories are formed, the DNA in some nerve cells snaps, triggering an immune response responsible for repair. This DNA damage-and-repair cycle might be a way for nerve cells to make memories that last. When mice were trained to remember an electrical shock, the nerve cells initiated an inflammatory response mediated by the TLR9 protein. When the researchers deleted the gene encoding the TLR9 protein from mice, the animals had trouble recalling long-term memories: they forgot the place where they had previously been shocked. These findings contribute to the picture that forming memories is a “risky business”, says neurobiologist Li-Huei Tsai.
Get the expert view from neuroscientists Benjamin Kelvington and Ted Abel in the Nature News & Views article (8 min read, Nature paywall)
Before the collapse of cryptocurrency exchange FTX and the jailing of its chief exec Sam Bankman-Fried, the company allocated tens of millions of dollars to effective altruism — a philanthropic movement dedicated to tackling long-term risks to humanity, such as climate change. This included giving money to research organizations and scientists, many of whom are under pressure to return the money. Some people are concerned that news of the fraud has damaged the perception of effective altruism itself. “We were really gearing up to this big change,” says Sawyer Bernath of the Berkeley Existential Risk Initiative. “All of a sudden it turned out to be all fake.”
Features & opinion
Efforts such as the Patient-Led Research Collaborative have played a crucial role in advising, designing and even funding basic and clinical research into long COVID. Its influential survey has amassed more than 1,000 citations. Co-founder Lisa McCorkell is among the patient advocates who say that despite the fact that such efforts can worsen their symptoms, they have little choice but to get involved. “We’re driven by desperation, out of improving our own quality of life.”
Reference: eClinicalMedicine paper
A spreadsheet that has been shared between graduate students around the world for more than a decade helps academics in management navigate the job market. Refreshed each year, the spreadsheet’s tabs act as a job-listings board — and a forum for questions and frustrations. “If that sounds similar to Slack and other messaging tools, it is,” writes business researcher Silvia Sanasi. “But the spreadsheet is completely anonymous. It is also incredibly flexible, quick to load and easy to search. Plus, researchers are already well versed in spreadsheets — and appreciate the ability to trawl job-search boards while looking as if they’re working.”
Palaeobotanist Estella Bergere Leopold’s investigations of fossil pollen and spores provided some of the first insights into the evolution of modern plant communities. In 1955, Leopold became one of the few female scientists at the US Geological Survey, where her studies revealed the existence of a tropical rainforest in the south Pacific millions of years ago. Leopold was also an ardent conservationist and activist who traced back her unbridled enthusiasm for ecology to her childhood spent on a farm in Wisconsin. “Without loving nature,” she said in 2011, “who’s going to want to protect it?” Leopold has died, aged 97.
A bird-like brain might have been the ancestral crucible for dreams, writes cultural curator Maria Popova. In ostriches, which belong to the most ancient group of birds, and platypuses, which are part of the most ancient mammal group, dream-like activity was found in the brainstem. In other birds and mammals, dream-rich sleep takes place primarily in the forebrain, suggesting that dreaming slowly migrated into this evolutionarily younger structure. “The most haunting intimation of the research on avian sleep is that without the dreams of birds, we too might be dreamless,” Popova says.
The New York Times | 8 min read
Image of the day
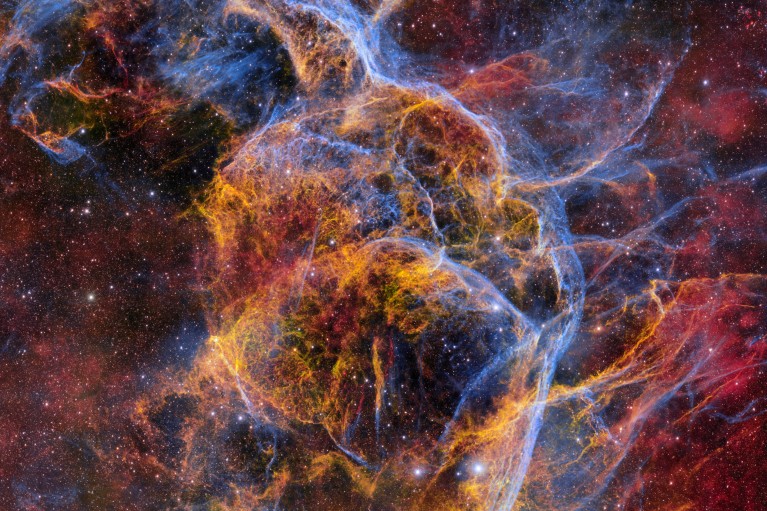

Credit: CTIO/NOIRLab/DOE/NSF/AURA; Image processing: T. A. Rector, Univ. Alaska Anchorage/NSF’s NOIRLab; M. Zamani & D. de Martin, NSF’s NOIRLab
This stunning photo shows the Vela supernova remnant, an expanding nebula of cosmic debris created by a massive stellar explosion around 11,000 years ago. The image was created by separately capturing light of distinct wavelengths using filters and then combining them.
See more of the month’s sharpest science shots, selected by Nature’s photo team.
On Thursday, Leif Penguinson was visiting the mangroves in the Princess Alexandra National Park on the Turks and Caicos Islands. Did you find the penguin? When you’re ready, here’s the answer.
Thanks for reading,
Flora Graham, senior editor, Nature Briefing
With contributions by Gemma Conroy, Katrina Krämer, Smriti Mallapaty and Sarah Tomlin
Want more? Sign up to our other free Nature Briefing newsletters:
• Nature Briefing: Anthropocene — climate change, biodiversity, sustainability and geoengineering
• Nature Briefing: AI & Robotics — 100% written by humans, of course
• Nature Briefing: Cancer — a weekly newsletter written with cancer researchers in mind
• Nature Briefing: Translational Research covers biotechnology, drug discovery and pharma
[ad_2]
Source Article Link

