[ad_1]
If you like to dig deeper into the stats on your best smartwatch, there’s a strong chance you may have come across one called VO2 Max. It can be called something different on different smartwatches. On the Apple Watch, it’s known as ‘cardio fitness’, while on Fitbits, it’s referred to as your ‘cardio fitness score’.
VO2 Max is a fitness metric that has been around for some time, but if you’ve been grappling with what it actually is, what it tells you, and whether you should care about it, we’re going to clear things up for you here. This is the lowdown on the key fitness metric, and why it might be something you should take more notice of.
What does VO2 Max stand for?
Firstly, let’s break down what VO2 Max actually stands for. It’s defined as the maximum (Max) rate (V) of oxygen (O2) your body absorbs during exercise.

What does VO2 Max actually mean?
In simplest terms, it’s about breathing and what happens during the breathing process while you’re exercising.
When you breathe in, you’re taking in oxygen. That oxygen is used to create energy to enable the body and organs to properly function.
One of those energy forms created is called adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. ATP is used as fuel for your muscles, and will help your body to better cope with the demands of exercise.
While you’re exercising, the body demands more oxygen to turn into those ATP reserves. The more oxygen you can take in and turn into that energy form, the better your body should be at reducing the onset of fatigue.
Having an insight like VO2 Max can tell you the maximum rate of oxygen you can absorb, to offer a good indication of the ATP energy levels your body can produce to keep you powering through your workout.

Why is knowing your VO2 Max useful?
VO2 Max is a useful stat because it offers a window into your cardiovascular fitness and aerobic endurance. The former relates to how well your heart and lungs can supply oxygen during exercise and the latter relates to your ability to handle exercise at moderate intensity over extended periods.
It’s going to tell you about your capabilities to tackle tough training schedules, events and races. It’s why athletes will look to attain a high VO2 Max to ensure their body is considered well-equipped to meet the demands of the pressures put on the body by more intense exercise associated with endurance sports like running a marathon, ultra marathon or doing a triathlon.
It’s not just about fitness here either. Maintaining a good VO2 Max can help you become more resilient to stress, help combat the effects of aging, and can also decrease your chances of getting ill.
How is VO2 Max measured on your smartwatch?
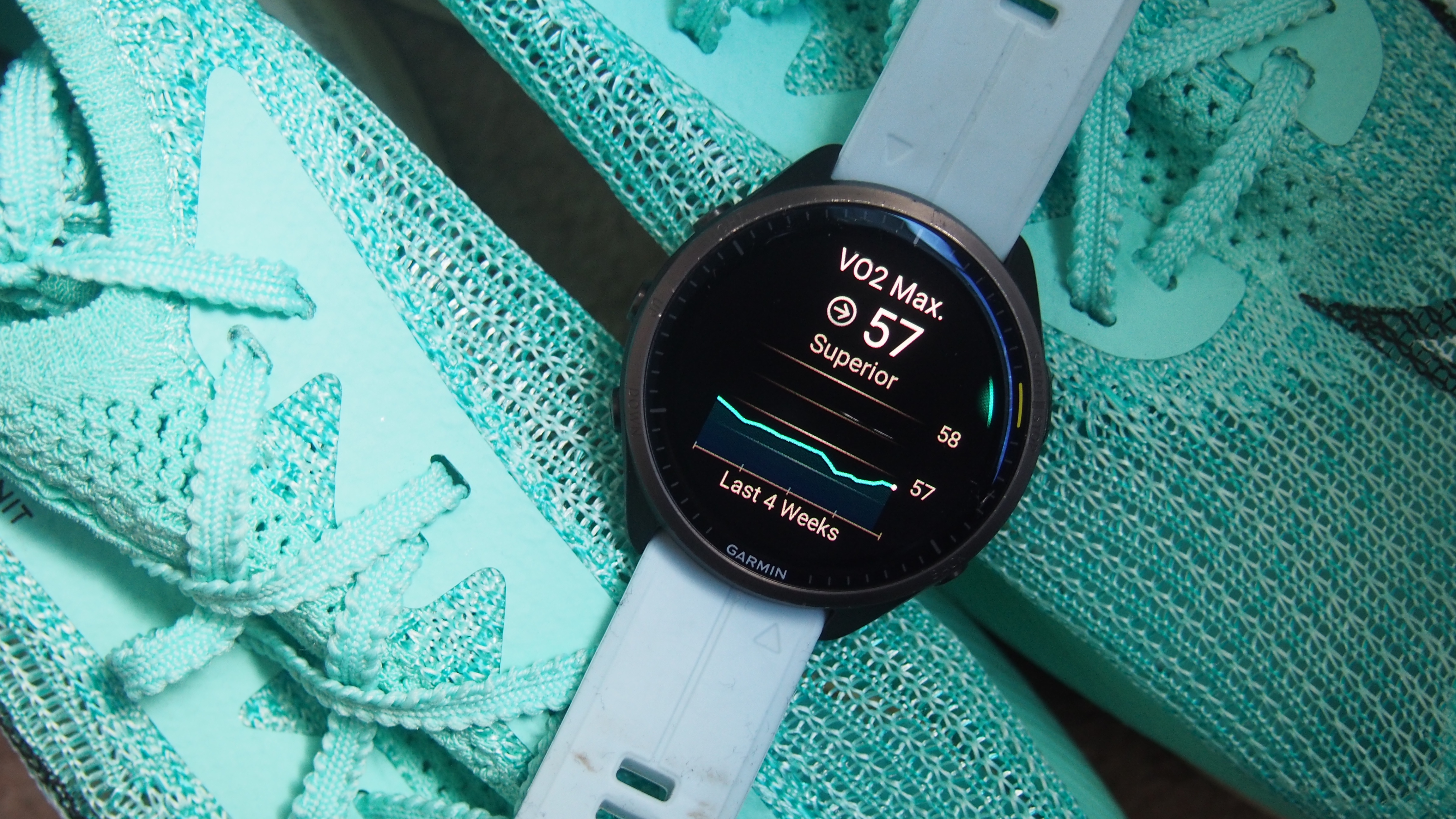
VO2 Max is typically measured in millimetres of oxygen consumed per kilogram of body weight per minute, and is typically represented as a single two-digit number. While there’s some inconsistency across how smartwatches present VO2 Max, having a higher VO2 Max score typically indicates someone with an excellent level of cardiovascular fitness.
The most accurate way to measure VO2 Max is from a lab test, where you’ll jump on a bike or treadmill,strap on a mask and work out until exhaustion to measure the air you consume and release. Watches are actually giving you an estimate of that VO2 Max, as most aren’t able to replicate that same rigorous lab testing process.
So, how accurate are those estimates? Firstbeat Analytics, which calculates the data for VO2 Max estimates on Garmin’s watches, claims an accuracy of 95%.
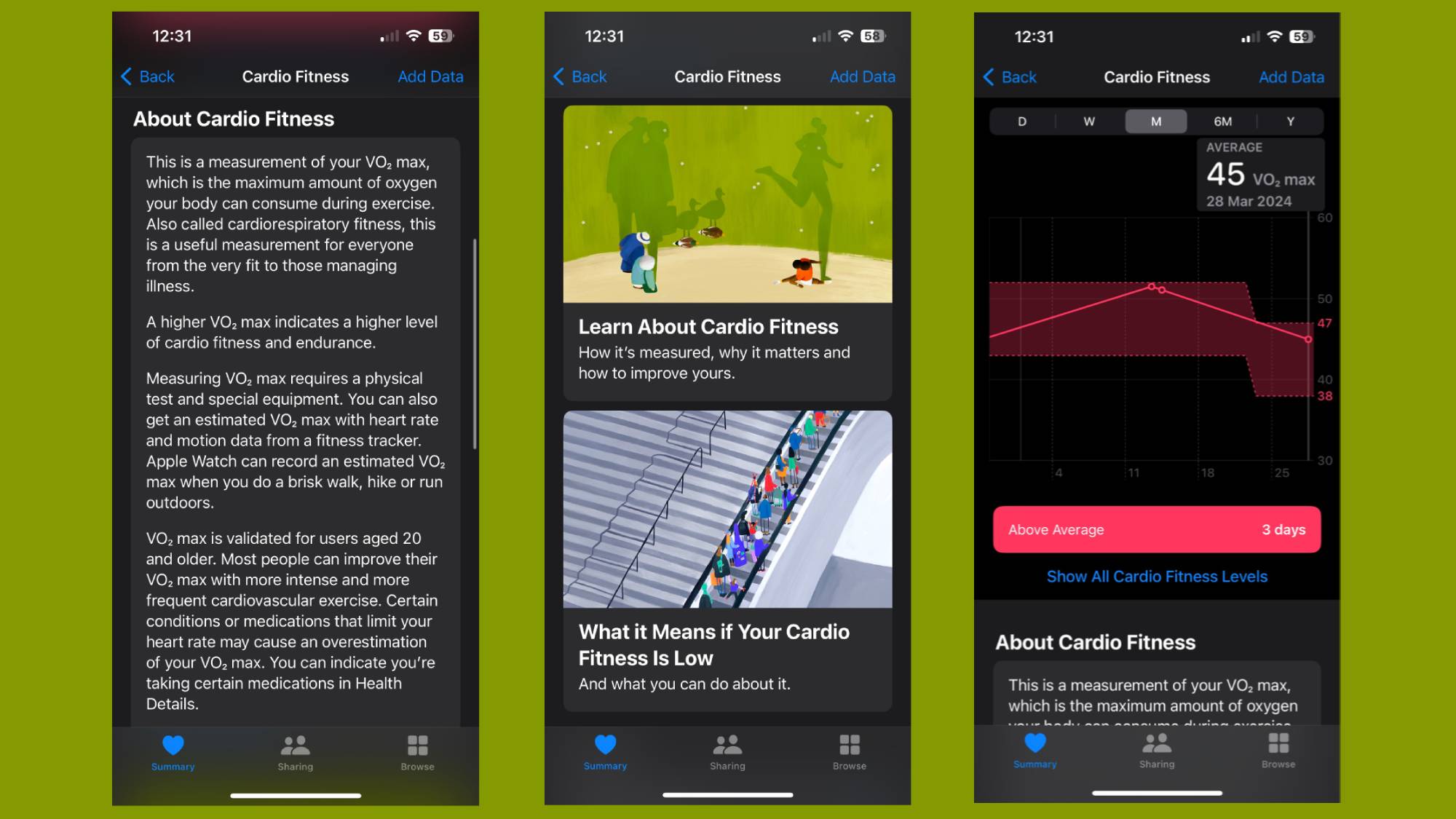
Apple estimates its VO2 Max estimates (known as cardio fitness) by using data from its heart rate sensors and motion sensors during outdoor runs, walks or hikes. It’ll also factor in elements like your age, sex, weight and height to produce a reliable VO2 Max score, which ranges from 14 to 65 mL/kg/min.

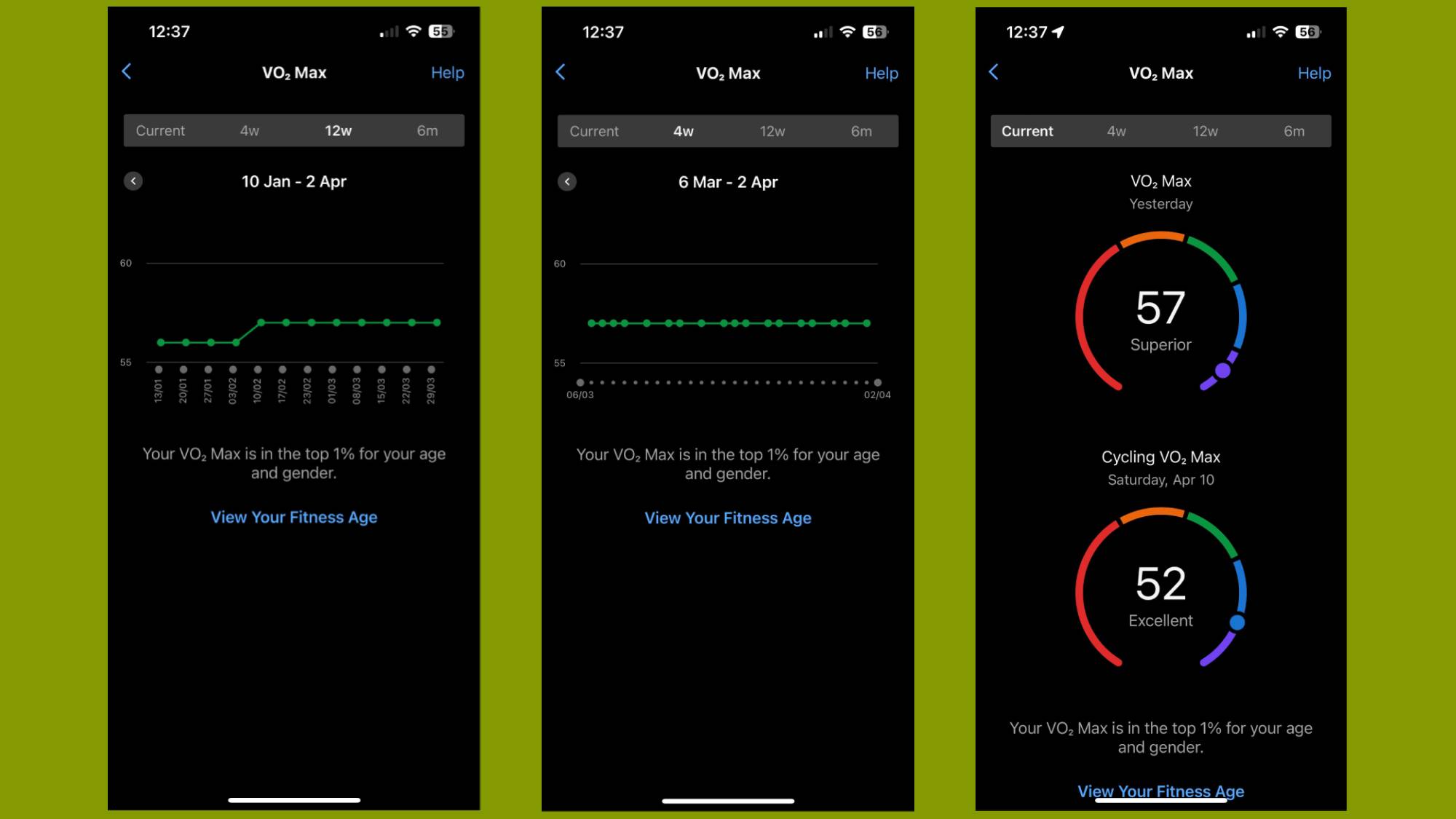
If you’ve got a Garmin watch, Garmin produces its VO2 Max estimates based on heart rate from your watch or an external heart rate monitor. It’s also generated from exercises lasting 10 minutes or longer. It looks at activities recorded outdoors using GPS and when heart rate is elevated to at least 70% of your maximum heart rate continuously for ten minutes.
Garmin’s VO2 Max score ranges from 0-95. The highest VO2 Max ever recorded was Bjørn Dæhlie, an Olympic skier, with 96. Although a good VO2 Max estimate depends on your age, height and weight, generally speaking, the higher the better. Garmin has a handy chart explaining what constitutes a “good” VO2 Max for your demographic.
The way those estimates are calculated can vary by exercise and the likes of Garmin is aiming to do a better job of factoring in how different activities and workout conditions can impact on VO2 Max measurements.

In the case of Google and Fitbit and its own VO2 Max scores known as cardio fitness score, it looks at resting heart rate, age, sex, weight and will provide more accurate scores when using your GPS to track workouts.
Fitbit breaks scores down into one of six levels. A 55 cardio fitness score is considered an excellent score and puts you in that top 6 level, while a 35 score is deemed average and puts you at level 3 on that scale.
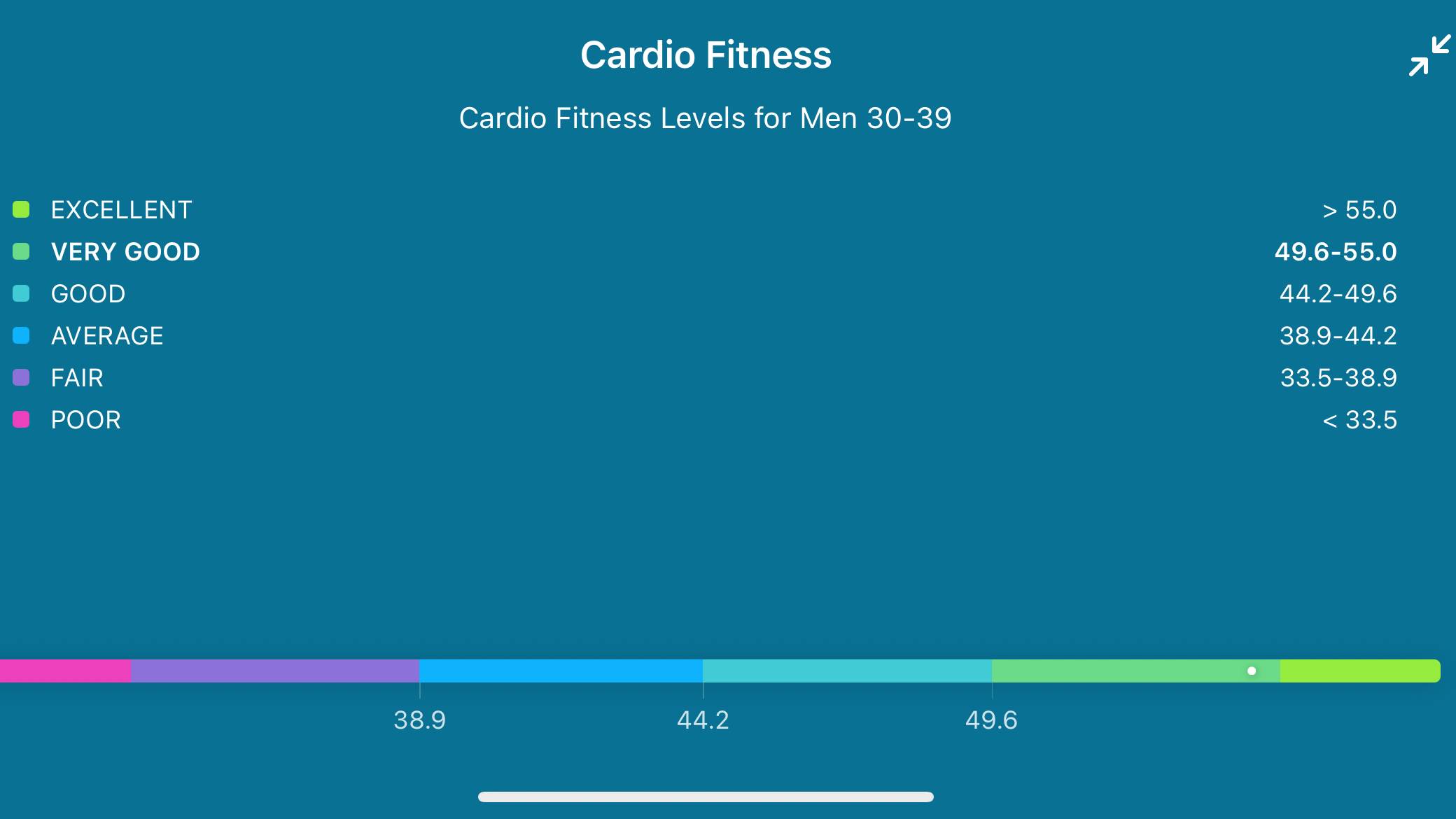
Where can you view VO2 Max on your smartwatch?
Again, this entirely depends on what smartwatch you’re using to try to view your VO2 Max stats. So in the case of the Apple Watch, Apple doesn’t natively show this information off on the Watch, instead tucking away inside of the Apple Health iPhone app. There are third party Apple Watch apps though that will let you view that data on the Watch if you do want to see it there.
The likes of the Samsung Galaxy Watch 6 will let you see measurements on the watch after workouts are completed in the Health section of the app while Fitbit hosts that information inside of the companion app when you click on the heart tile on the Today section of its app to delve into its Cardio Fitness scores.
For Garmin users, you’ll be able to see current and historical VO2 Max data in the performance stats section of the Garmin Connect app. You can also view it on the watch from the Training Status widget.
Why are VO2 Max scores different across smartwatches?
While the core approach that smartwatches calculate VO2 Max estimates will largely be the same, the heart rate sensors (sensor accuracy) and algorithms that help to throw up that data may not be. These can be big factors as to why you might see different numbers across watches.
There’s also the subject of how much historical workout data the smartwatch has had access to, which can influence the reliability of those VO2 Max numbers as well.
How can you improve VO2 Max?
That is the big question and one that has a few simple answers. The most straightforward one is increasing the amount of exercise you do on a regular basis, paying close attention to the intensity of that exercise time.
High intensity interval training (HIIT) during which you’re quickly spiking heart rate and then resting and recovering, gets the body more accustomed to the increased demand of oxygen. This strengthens muscles and helping the body to adapt to handle more intense exercise. There have been studies conducted examining how this type of training can give VO2 Max estimates a boost.
Low-intensity training can do the trick as well, so activities like running, cycling or hiking and mixing up those low-intensity activities can also be routes to an improved VO2 Max. It’s why runners training for marathons and sticking to those regular runs and long runs can see an uptick in their VO2 Max and increase their capacity to endure tougher bouts of exercise.
Recovery time in between workouts is also as important as doing the workouts, as your body needs time to adapt to the increased demands of more intense exercise.
[ad_2]
Source Article Link

