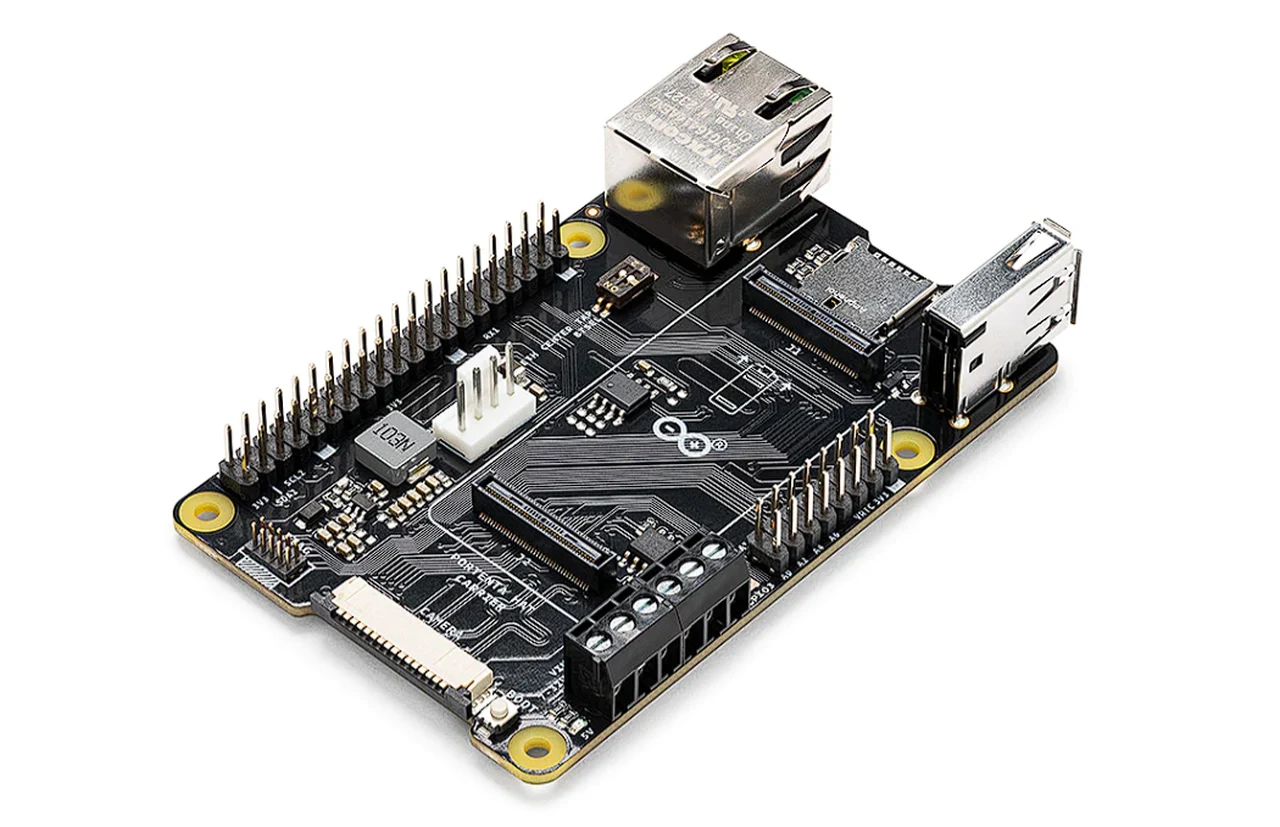
The official Arduino development team has this week announced the arrival of the new Arduino Pro Portenta Hat Carrier. A carrier board compatible with Raspberry Pi Hats and cameras, offering a significant development in the world of single board computers.
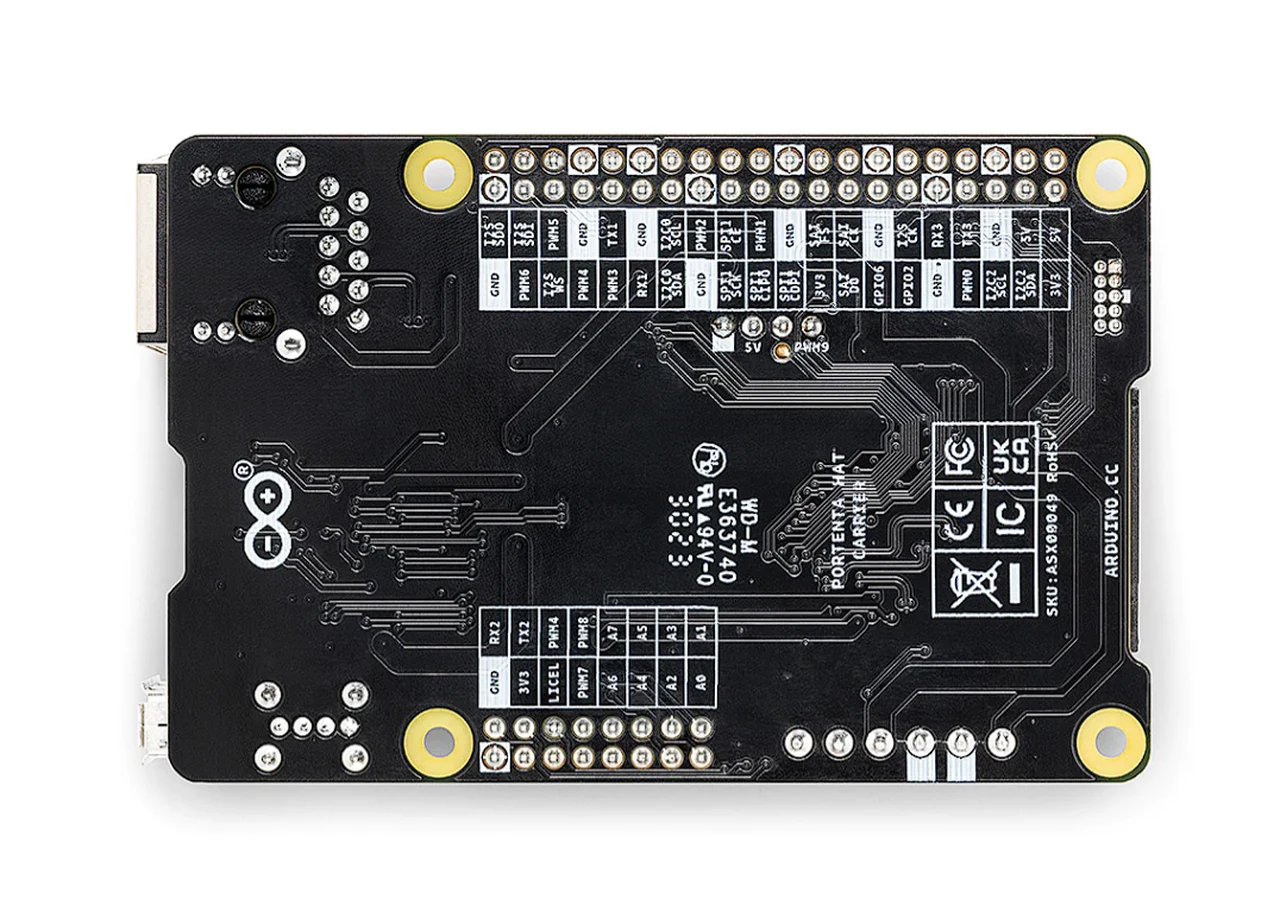
The Portenta Hat Carrier provides easy access to multiple peripherals such as CAN, Ethernet, microSD, and USB. This makes it suitable for both prototyping and scaling up, extending the features of a typical Raspberry Pi Model B. With dedicated JTAG pins for quick debugging and a PWM fan connector for efficient heat management, this carrier board is designed for ease of use and high performance.
On-board camera connector
One of the standout features of the Portenta Hat Carrier is its onboard camera connector, which enables the addition of industrial machine vision solutions. This feature, combined with the ability to control actuators or read analog sensors via 16 additional analog I/Os, makes the carrier board a powerful tool for a variety of applications.
Availability and pricing
The Portenta Hat Carrier is available for €39 or $45 in the Arduino Store and through major distributors. It offers a frictionless Linux prototyping experience and the ability for integrated real-time MCU solutions, making it an affordable and efficient option for those looking to develop advanced commercial solutions.
Arduino Portenta Hat Carrier
“Portena Hat Carrier provides a unique bridge between the Arduino and Raspberry Pi ecosystems, offering professionals a modular platform for prototyping to full-fledged industrial applications,” said Massimo Banzi, Arduino’s co-founder, chairman and CMO. “We are excited to offer a product that answers our customers’ requests and supports an ecosystem we admire.”
Other articles we have written that you may find of interest on the subject of Arduino hardware and projects :
The Portenta Hat Carrier is designed to combine and extend MPU and MCU applications, which is a key benefit of using it. The integration with the Arduino and Raspberry Pi ecosystems also makes it a versatile tool for developers. Its compatibility with a wide range of Raspberry Pi HATs and the ease of debugging and inspecting the CAN lines through dedicated pins further add to its appeal.
The carrier board enables any Portenta module easy expansion to multiple peripherals, including any Raspberry Pi HAT compatible with the Model B 40-pin header, Ethernet, microSD, and USB. It also features an onboard CAN transceiver, an additional 8x analog I/Os, and a PWM fan connector.
The Portenta Hat Carrier is suitable for industrial applications ranging from robotic motion controls, intelligent sorting, anomaly detection, vehicle monitoring, and smart sensing. Its wide range of compatible peripherals, easy debugging and inspection capabilities, and additional analog I/Os and a PWM fan connector make it a robust and versatile option for a variety of industrial applications.
The Portenta Hat Carrier is a carrier board that offers a wide range of capabilities, making it a valuable tool for developers and industries alike. Its compatibility with Raspberry Pi Hats and cameras, along with its multiple peripherals and extension of features found in the Raspberry Pi Model B, make it a powerful and versatile addition to the Arduino PRO range. Its affordability and ease of use, combined with its suitability for commercial and industrial applications, make it a compelling choice for those looking to extend their single board computer capabilities.
Filed Under: Hardware, Top News
Latest timeswonderful Deals
Disclosure: Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, timeswonderful may earn an affiliate commission. Learn about our Disclosure Policy.

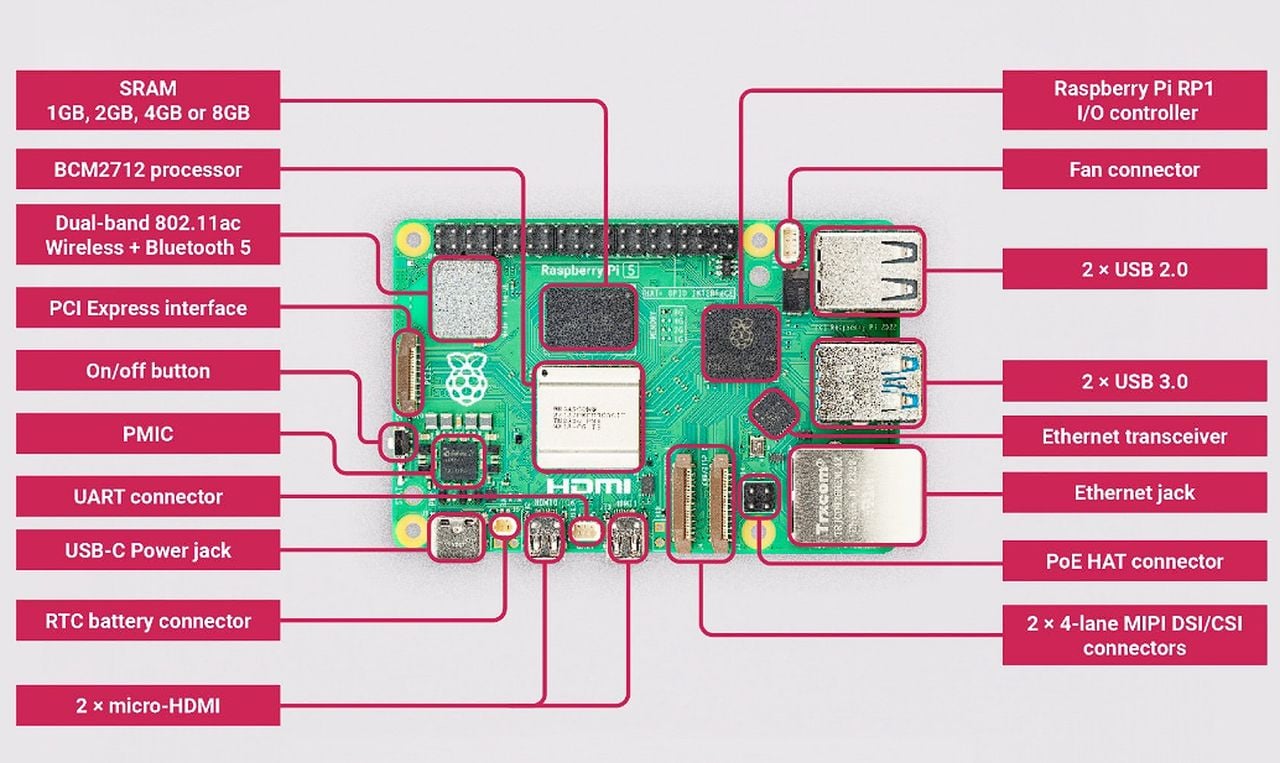
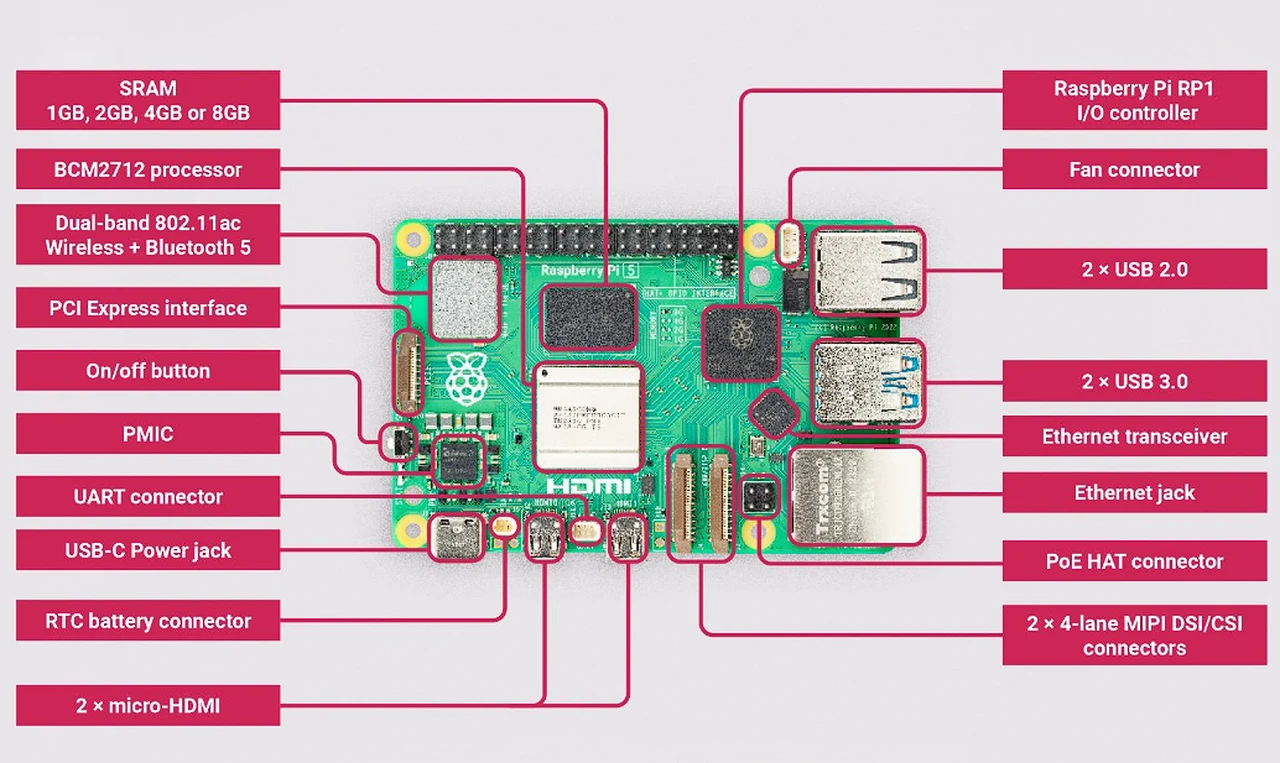

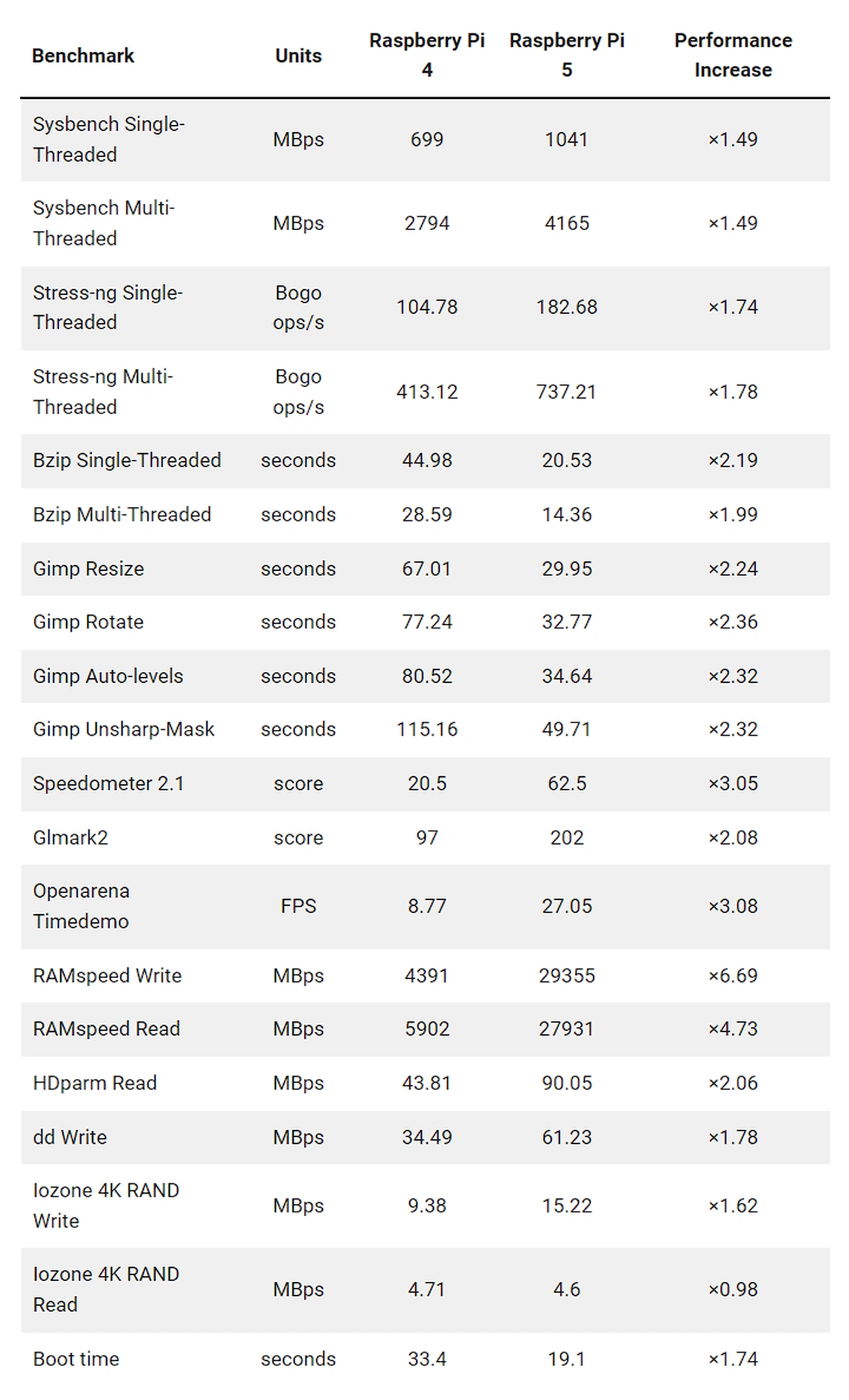




 The last week or so the official Raspberry Pi development team rolled out a new version of its Raspberry Pi OS operating system now featuring Debian Bookworm. The update is an incremental update from the previous Debian Bullseye release but marks a significant milestone in the evolution of the Raspberry Pi ecosystem, introducing major architectural changes that promise to enhance performance, security, and user experience. However if you have a Orange Pi Zero 3 mini PC you might be interested to know that you can run the older Raspberry Pi OS Bullseye operating system on it with success.
The last week or so the official Raspberry Pi development team rolled out a new version of its Raspberry Pi OS operating system now featuring Debian Bookworm. The update is an incremental update from the previous Debian Bullseye release but marks a significant milestone in the evolution of the Raspberry Pi ecosystem, introducing major architectural changes that promise to enhance performance, security, and user experience. However if you have a Orange Pi Zero 3 mini PC you might be interested to know that you can run the older Raspberry Pi OS Bullseye operating system on it with success.