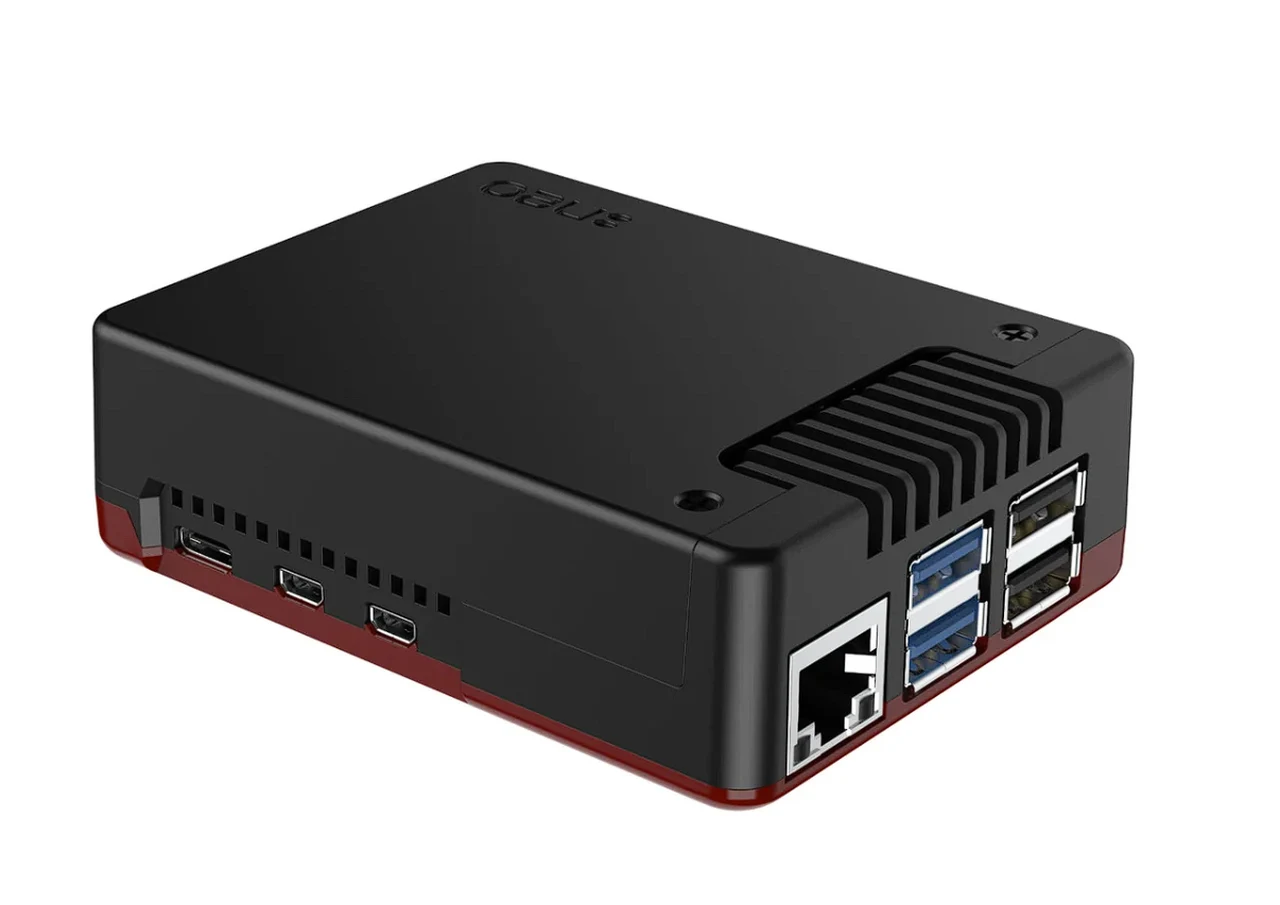
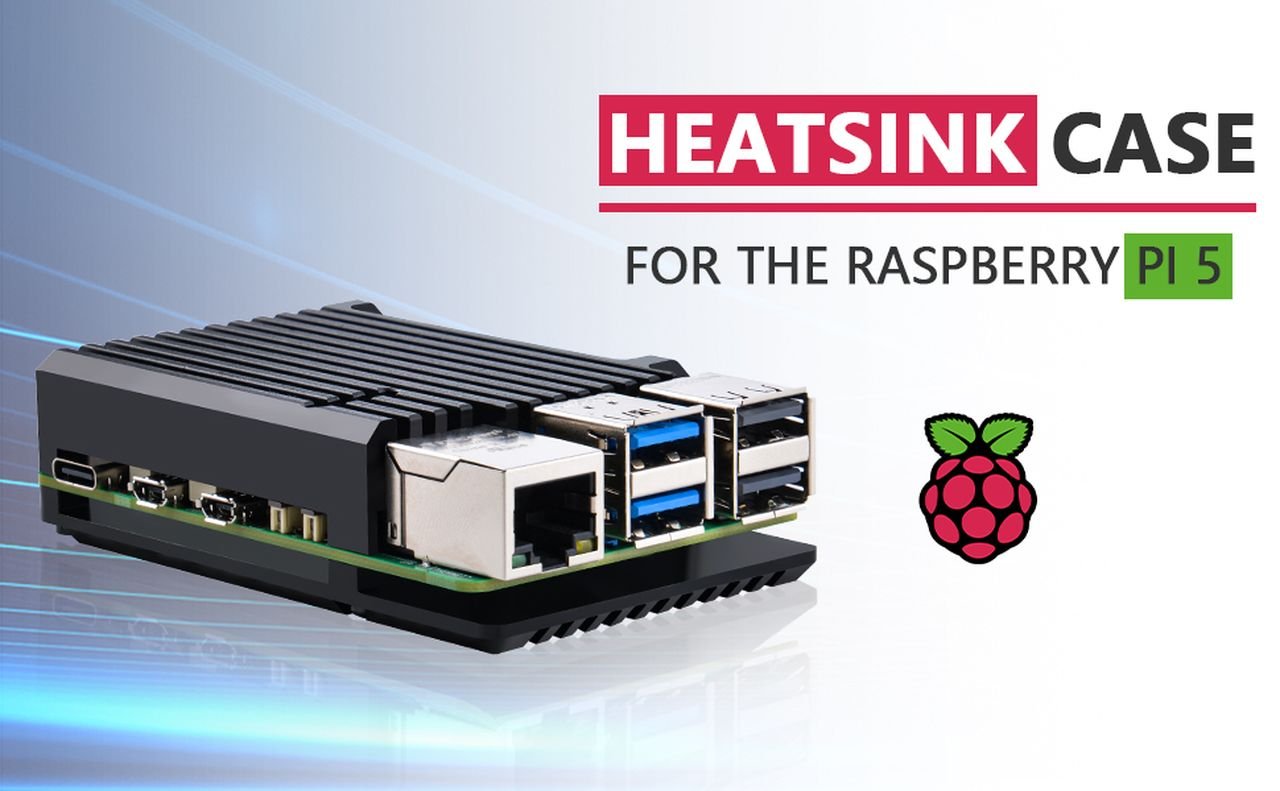
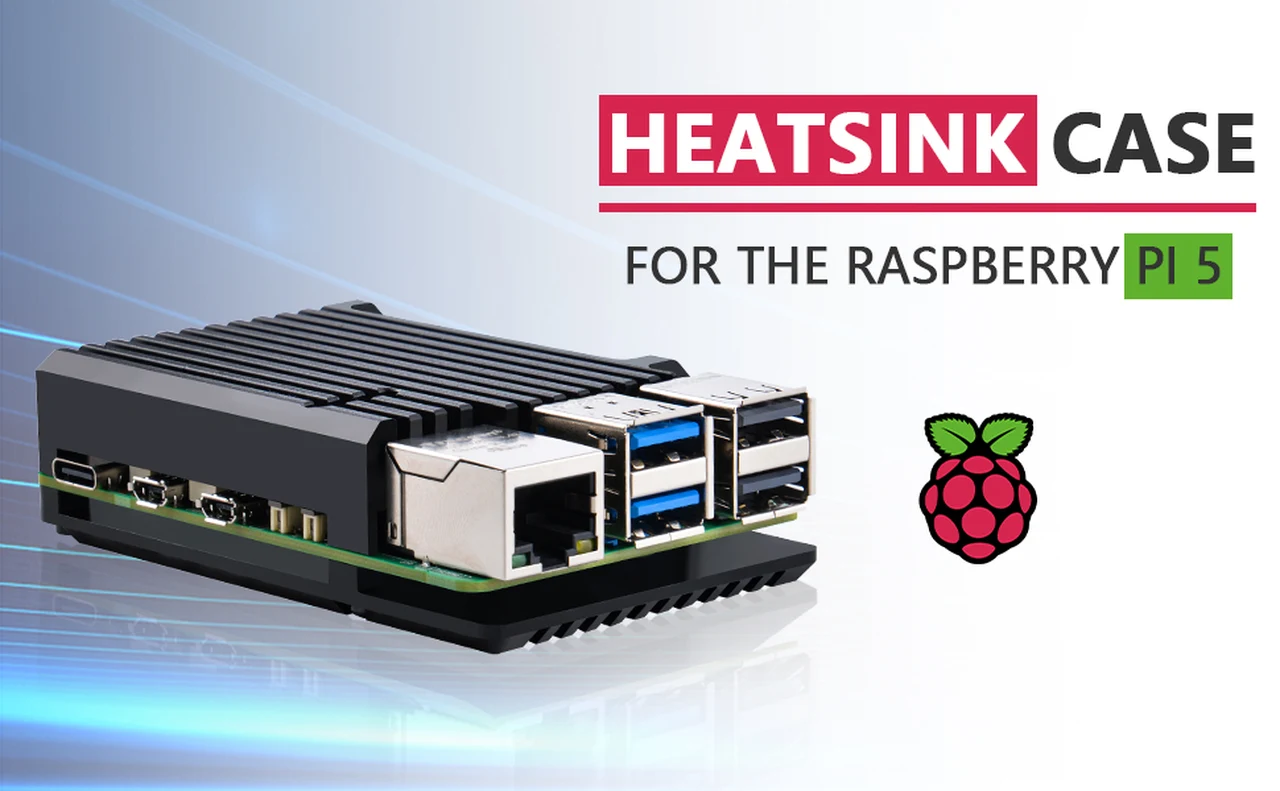
For enthusiasts and professionals who use the Raspberry Pi 5, the Argon NEO 5 BRED case is a significant upgrade that combines enhanced cooling with a sleek design. This case is not just about giving your device a new look; it’s about improving its functionality and ensuring it runs smoothly under any workload.
Crafted from aluminum, the Argon NEO 5 BRED case acts as a passive cooling system. Its design includes cooling fins that effectively dissipate heat, which is crucial for maintaining the Pi 5’s performance during intensive tasks. For users who need even more cooling power, the case comes equipped with a 30mm PWM fan. This fan, along with the strategically placed air intake vents, works to boost airflow and heat transfer, keeping your device at the ideal operating temperature.

The case is designed with user convenience in mind, offering easy access to all the necessary I/O ports. A special feature is the Micro SD card cover, which allows for quick and secure storage media changes. Additionally, the case has rubber feet to prevent slipping and to provide stability on a variety of surfaces.
Raspberry Pi 5 case : Argon NEO 5 BRED
Here are some other articles you may find of interest on the subject of the Raspberry Pi 5 mini PC
Installation of the Argon NEO 5 BRED case is a simple process. The package includes thermal pads that help transfer heat from the Pi 5 to the case efficiently. The assembly is user-friendly, with a straightforward screw design that lets you set up your device quickly and without any complications.
Optimize the power of Pi 5
- The Argon NEO 5 is redesigned specifically to meet the high demands of the Raspberry Pi 5.
- Impressive thermal dissipation solution for both passive and active cooling.
- Aluminum case enclosure with passive cooling fins that act as the heatsink
- Air intake vents allow for cool air to enter the case
- 30mm PWM fan helps with the airflow and push out hot air to exhaust vents
Simple and beautifully designed
- Made with aluminum alloy and polished with a Black & Red finish for stunning aesthetics.
- Easy assembly for the 3 part case with the Raspberry Pi 5.
- Small foot print allows to bring it anywhere – or easily mount to your desired station with built in mounting points.
- Complete access to all ports with the removable top cover.
Superior protection & security
- Space grade aluminum helps protect Raspberry Pi 5 board from physical damage.
- The case has a screw on top cover to keep the ports safe when not in use.
- Optional SD card cover to protect your data even further.
Native Raspberry Pi 5 board support
- Integrated power button
- LED light display
Tests have shown that the Argon NEO 5 BRED case is effective at keeping the Pi 5 cooler than when it is used without any additional cooling measures. It performs on par with the official active cooler from the Raspberry Pi Foundation, offering reliable thermal management.
When considering the cost, the Argon NEO 5 BRED case is an affordable option for those looking to upgrade their Raspberry Pi 5 experience. The aluminum construction is not only functional for cooling purposes but also provides a professional appearance that can enhance the look of your workspace.
Overall, the Argon NEO 5 BRED Raspberry Pi 5 case is a smart choice for anyone who uses the amazing mini PC for various projects, whether they are hobbyists, professionals, or educators. It ensures that your device stays cool, operates efficiently, and looks good doing it.
Filed Under: DIY Projects, Hardware
Latest timeswonderful Deals
Disclosure: Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, timeswonderful may earn an affiliate commission. Learn about our Disclosure Policy.
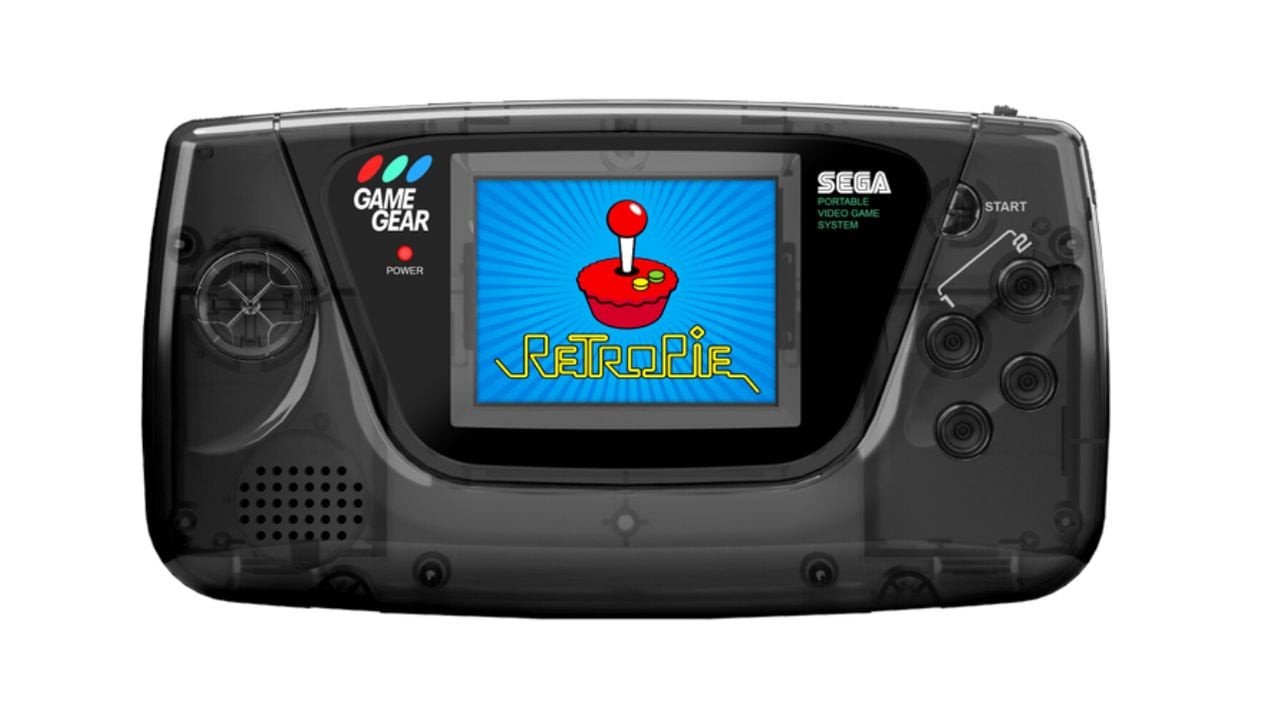


 The nostalgia of the Sega Game Gear is undeniable for those who grew up in the ’90s, but imagine taking that sentiment and infusing it with today’s technology. This is exactly what happened when a defunct Game Gear that was revitalized using a Raspberry Pi, the already iconic credit-card-sized computer that has become a staple in modern DIY electronics projects.
The nostalgia of the Sega Game Gear is undeniable for those who grew up in the ’90s, but imagine taking that sentiment and infusing it with today’s technology. This is exactly what happened when a defunct Game Gear that was revitalized using a Raspberry Pi, the already iconic credit-card-sized computer that has become a staple in modern DIY electronics projects.