If you have ever dreamt of owning your own precision robotic arm you might be interested in the MyCobot 280 Pi. An advanced robotic arm that is powered by the Raspberry Pi mini PC and is reshaping the way we think about automation and education. With a price tag of £651/$799, this piece of technology is making sophisticated robotics more accessible than ever before. It’s a tool that’s not just for experts but for anyone with a passion for innovation and learning.
“Using Raspberry Pi microprocessor and Ubuntu Mate 20.04 operating system, myCobot 280 Pi can be used by connecting monitor, keyboard and mouse without PC master control. It is the first choice for building robot arm programming education, control logic development, robot application and ROS simulation experiment class. To help you quickly start the learning and application of six axis robotic arm.”
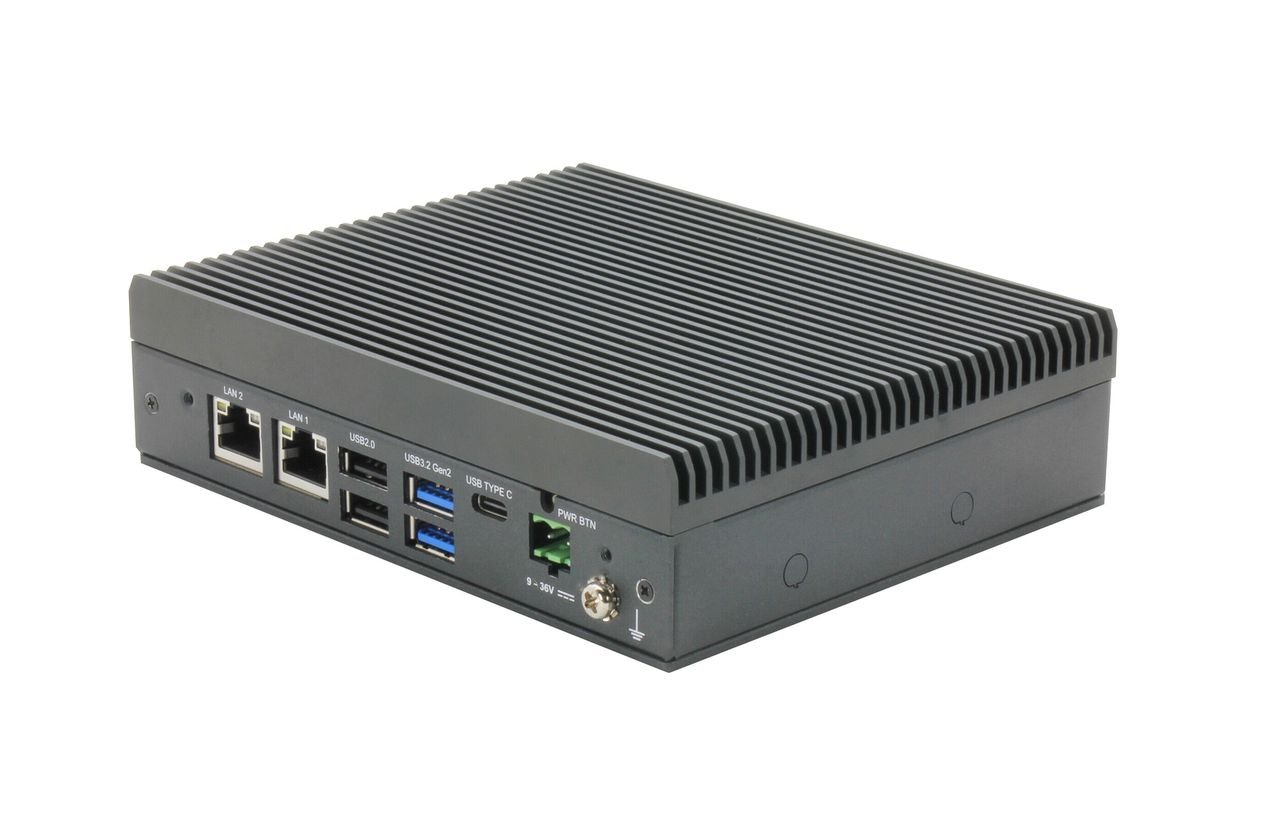
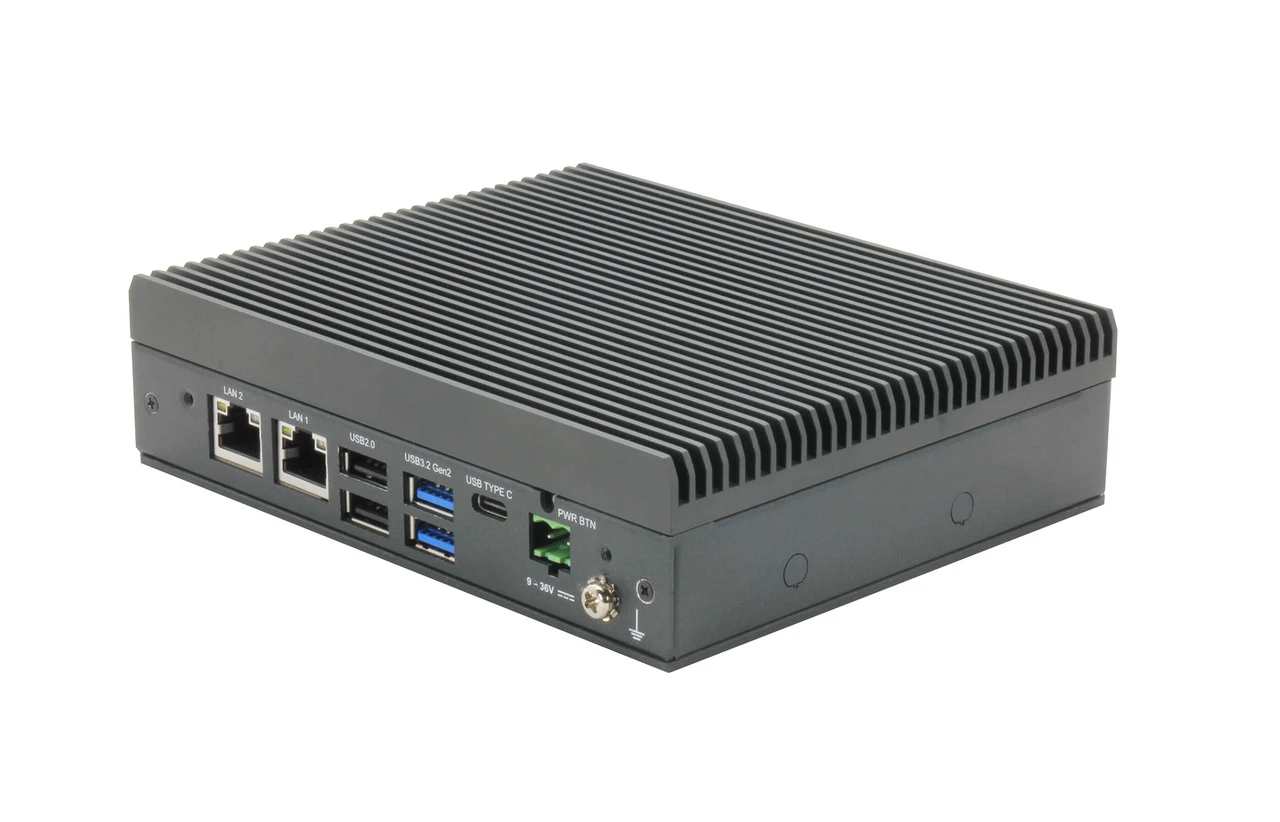
The MyCobot 280 Pi is a marvel of modern engineering, boasting a 330° working rotation arc and a reach of 280mm. This robotic arm is not just about its physical capabilities; it’s also about the brains behind its operation. At its core is the Raspberry Pi 4, a tiny but powerful computer that provides the MyCobot 280 Pi with its intelligence and connectivity. This integration allows the robotic arm to perform a wide range of tasks with precision and ease, making it an invaluable asset for those looking to delve into the world of robotics.
What sets the MyCobot 280 Pi apart is its six degrees of freedom. This means the arm can move in six different ways, allowing for intricate and precise movements that mimic the dexterity of a human arm. This level of control is essential for tasks that require a delicate touch, such as assembling small components or conducting detailed experiments. The arm’s flexibility is further enhanced by its compatibility with various programming languages and the Robot Operating System (ROS), which is widely used in robotics research and development.
Raspberry Pi robotic arm
The MyCobot 280 Pi is not just about its technical prowess; it’s also designed with longevity in mind. Its durable plastic casings protect the internal components, ensuring that the robotic arm can withstand the rigors of continuous use. This durability is crucial for educational environments, where the arm may be used by multiple users and subjected to frequent handling.
Here are some other articles you may find of interest on the subject of Raspberry Pi 5 :
In terms of design, the MyCobot 280 Pi is both functional and adaptable. Its six joints provide a wide range of motion, and the inclusion of LEGO connectors opens up a world of possibilities for customization. Users can easily attach accessories and bases, allowing the robotic arm to take on new forms and functions. The G-Base 2.0 ensures that the arm remains securely attached to a desk or work surface, providing a stable foundation for all activities.
The MyCobot 280 Pi’s performance is not limited to a single application. It has proven itself capable of handling a variety of tasks with exceptional precision. This versatility has led to its widespread adoption, with over 10,000 units sold in more than 50 countries. The robotic arm supports over 10 accessories, making it suitable for complex projects in commercial exhibitions and educational settings. Its ability to engage and inspire is evident in the diverse ways it is being used around the world.
MyCobot 280 Pi
When it comes to technical specifications, the MyCobot 280 Pi is well-equipped to handle a range of items with its payload capacity of up to 250g. It features multiple connectivity ports, including USB 3.0, USB 2.0, Ethernet, and micro-HDMI, which provide users with the flexibility to connect a variety of peripherals. Additional connectors like Grove and servo ports further expand the arm’s capabilities, allowing it to interface with an even broader array of devices and sensors.
The MyCobot 280 Pi stands out in the robotics market for its robust build, powerful servos, and versatile programming capabilities. It’s an exceptional choice for anyone looking for a sophisticated Raspberry Pi robotic arm that can meet the demands of both educational and professional environments. Whether you’re a teacher looking to bring robotics into the classroom, a researcher exploring new automation techniques, or a hobbyist eager to experiment with cutting-edge technology, the MyCobot 280 Pi offers a unique opportunity to engage with the world of robotics in a hands-on and meaningful way.
Designing and using robotic arms
A robotic arm is a type of mechanical arm, usually programmable, with similar functions to a human arm. The arm may be the sum total of the mechanism or may be part of a more complex robot. The links of such arms are connected by joints allowing either rotational motion (such as in an articulated robot) or translational (linear) displacement. The links of the arm are connected by joints to provide rotational motion.
In their design, robotic arms can vary greatly in size, shape, and capability. They range from small, precise devices used in medical and electronic applications, to large, industrial machines capable of lifting heavy loads. The complexity of the arm depends on the task it is designed to perform, with more complex tasks requiring more sophisticated control systems.
The control of robotic arms involves several key aspects. Firstly, the kinematics, which is the study of motion without considering the forces that cause it. This involves calculating the positions, velocities, and accelerations of the various parts of the robotic arm. Secondly, dynamics, which considers the forces that cause the motion, is crucial for understanding how the arm will react under different conditions. Lastly, control systems are used to manage the arm’s movements in a precise and intentional manner.
Robotic arms are used in numerous applications, including manufacturing, medical surgery, and space exploration. In manufacturing, they can perform tasks like welding, assembly, and material handling. In medicine, they assist in precise surgical procedures, often enhancing the capabilities of human surgeons. In space, robotic arms are essential for tasks like repairing satellites or moving cargo and equipment in environments where human activity is limited or impossible.
The development and use of robotic arms continue to evolve, incorporating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance their capabilities, efficiency, and adaptability to various tasks.
This robotic arm is more than just a tool; it’s a gateway to understanding and harnessing the power of robotics. It’s an invitation to explore, to create, and to innovate. The MyCobot 280 Pi is not just about what it can do today but about the potential it unlocks for tomorrow. As we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible, the MyCobot 280 Pi stands ready to be a trusted companion on that journey, bringing the future of robotics within reach for all. If you enjoyed Raspberry Pi projects you might also be interested in knowing how to run artificial intelligence (AI) on a Raspberry Pi 5 using Ollama.
Filed Under: Hardware, Top News
Latest timeswonderful Deals
Disclosure: Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, timeswonderful may earn an affiliate commission. Learn about our Disclosure Policy.