Over the past decade 3D printing has advanced from simple plastic objects to creating intricate designs with multiple materials to bioprinting living tissues, the possibilities are expanding rapidly, reshaping industries and sparking creativity. One of the most intriguing breakthroughs is Rapid Liquid Printing (RLP).
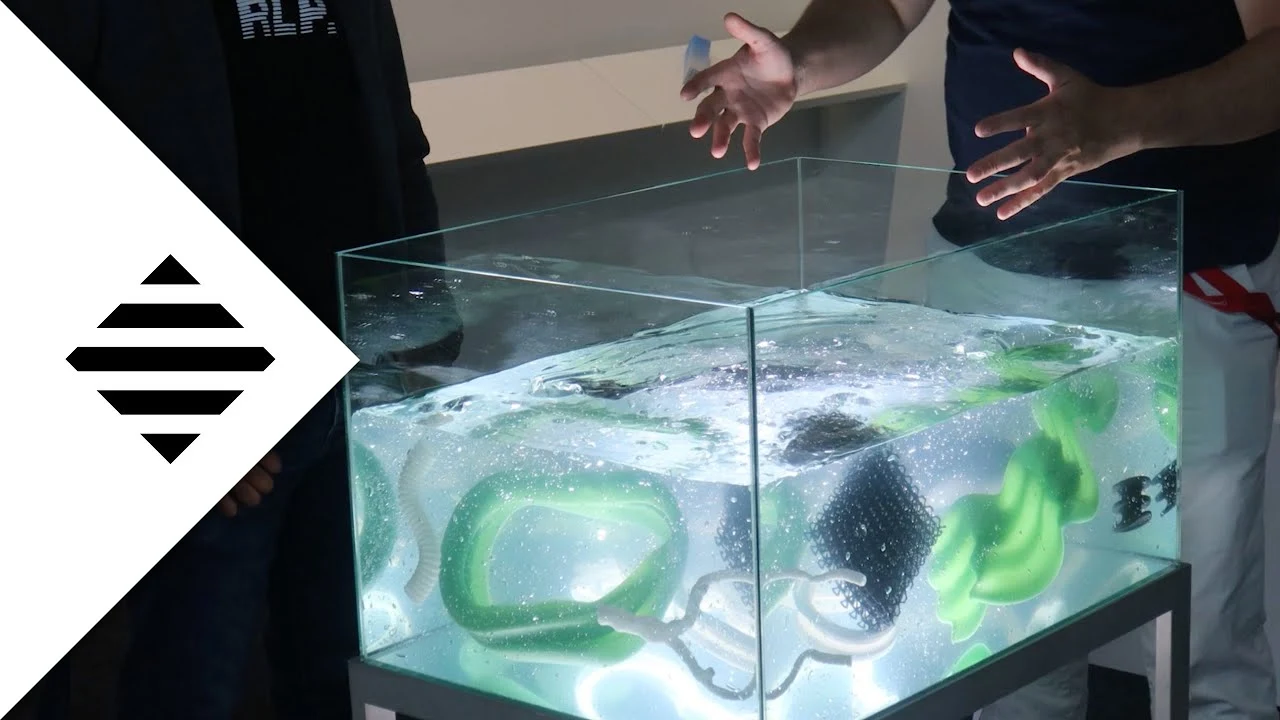
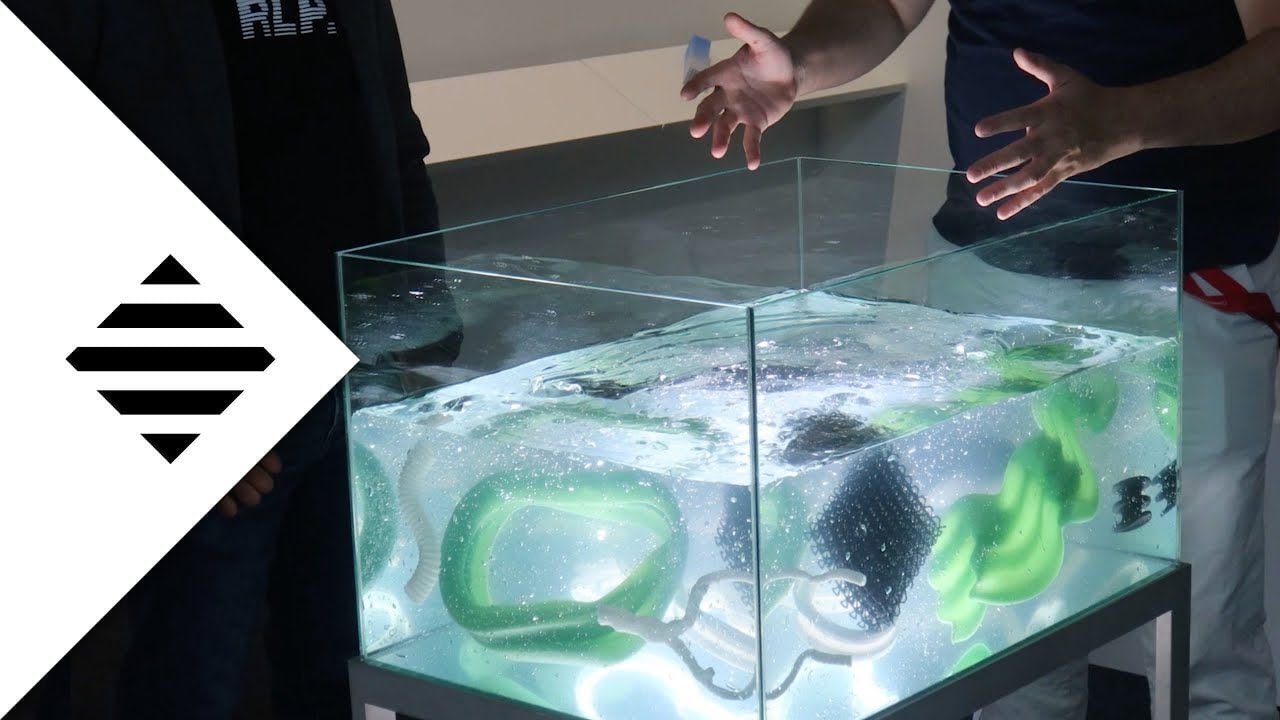
Rapid Liquid Printing (RLP) is an innovative 3D printing technique that significantly differs from conventional 3D printing methods. Unlike traditional 3D printing, which often involves building an object layer by layer from the bottom up, RLP involves printing within a gel suspension. This method allows for the creation of complex, soft shapes that were once thought impossible to produce. Unlike traditional 3D printing, RLP doesn’t require support structures, which means less material is wasted, and the process is more efficient. This could lead to a significant reduction in production costs and time, making it a valuable asset for manufacturers.
Rapid Liquid Printing
Rapid Liquid Printing is a groundbreaking technique from MIT’s Self-Assembly Lab. It’s a new way of 3D printing where you create objects in a gel, making them in three dimensions. The great thing is, as the object is made, it hardens and becomes ready to use almost right away, with hardly any extra work needed. This method is super fast at making big items out of top-notch materials like rubber, foam, and plastic. Traditional 3D printing can be slow, only make small things, and sometimes the materials aren’t that great. But Rapid Liquid Printing changes all that, allowing for the quick making of big, stretchy, airtight, and high-quality items.
Here are some other articles you may find of interest on the subject of 3D printing :
Here’s a breakdown of its key aspects and benefits compared with more traditional 3D printing technologies.
- Printing Medium: The gel-like medium in which RLP operates serves a dual purpose. Firstly, it supports the printed material during the printing process, eliminating the need for additional support structures typically required in traditional 3D printing. This feature allows for more complex and intricate designs to be printed. Secondly, the medium significantly reduces the effects of gravity, enabling the creation of smoother and more precise structures. The composition of the gel is carefully formulated to balance viscosity and density, providing an ideal environment for the printing material to solidify correctly.
- Materials: RLP’s ability to work with a variety of materials like plastics, rubbers, and foams broadens its application scope. This versatility is crucial for industries that require specific material properties, such as flexibility, durability, or lightweight structures. For instance, in the shoe industry, the use of different materials can lead to the production of custom footwear tailored to individual comfort and performance needs. Similarly, in furniture design, the use of varied materials can result in innovative, ergonomic, and aesthetically pleasing products.
- Speed: The speed of RLP is one of its most significant advantages over traditional 3D printing methods. While standard 3D printers may take hours or even days to complete an object, RLP can produce the same in a fraction of the time. This efficiency is achieved through the continuous extrusion of the printing material and the rapid curing process facilitated by the medium. Such speed is particularly beneficial in a commercial setting, where time efficiency translates to cost-effectiveness and quicker time-to-market for products.
- Precision and Scale: RLP offers remarkable precision, which is a critical factor in applications where detail and accuracy are paramount. Moreover, the scalability of RLP is notable, as it can create small, intricate objects as well as larger items, like furniture pieces. This scalability is a significant advancement over traditional 3D printing technologies, which often struggle with larger sizes due to limitations in printer bed size and structural integrity issues.
- Applications: The diverse applications of RLP span across various industries. In the fashion industry, it enables the creation of custom-fit apparel and accessories. In furniture manufacturing, RLP can produce unique, ergonomic designs that are both functional and aesthetically appealing. Additionally, its application extends to the automotive and aerospace industries for the production of customized, lightweight parts.
- Innovation and Future Potential: RLP is a groundbreaking development in additive manufacturing, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in terms of design complexity, material diversity, and production speed. Its future potential includes the possibility of even more materials being compatible with the technology, further increasing its versatility. There’s also potential in combining RLP with other manufacturing technologies and automation to create highly efficient, integrated production systems. The environmental impact of RLP, particularly in terms of material usage and waste reduction, is another area of future exploration, potentially making it a more sustainable manufacturing option.
Another innovation that’s catching the eye of experts is Multimaterial 3D Printing. Imagine printing a part that combines the hardness of metal with the flexibility of plastic in one seamless process. Researchers have developed a way to do just that, using a laser scanning system that works with slow-curing polymers. This could revolutionize how we create customized components for various applications, from medical devices to automotive parts.
In the realm of biotechnology, the 3D Bioprinting of Hair Follicles stands out as a significant achievement. Scientists have succeeded in bioprinting hair follicles within lab-grown skin, a development that could transform skin grafting procedures and potentially reduce reliance on animal testing. This is a big step forward in regenerative medicine and could lead to new treatments for burn victims and those with hair loss conditions.
The field of electronics is also benefiting from 3D printing, particularly in Micromanufacturing. A new metal 3D printer can create custom probes and test pads for microchip designs with incredible precision. This technology is essential for the development of smaller, more powerful electronic devices and could accelerate the pace of innovation in the semiconductor industry.
In the world of design and entertainment, Generative AI is transforming 3D modeling. A new tool can create realistic 3D human models from a single photo, which has vast implications for gaming, virtual reality, and online shopping. This technology could make digital content creation more accessible and personalized.
Lastly, the ability to produce DIY Optical Lenses using 3D printing is a testament to the technology’s versatility. Enthusiasts and professionals can now craft custom optics at a fraction of the traditional cost, opening up opportunities for innovation in photography, filmmaking, and scientific research.
These advancements in 3D printing and technology are reshaping our world in profound ways. They are not just fascinating; they represent a shift towards a future where innovation continuously pushes the boundaries of what’s possible. As we explore these developments, we can expect to see even more remarkable applications that will influence how we live, work, and play. As always we will keep you up to speed on all the latest technologies and advancements in 3D printing and AI technologies as well as gadgets and more.
Image Credit : MOSFET
Filed Under: Technology News, Top News
Latest timeswonderful Deals
Disclosure: Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, timeswonderful may earn an affiliate commission. Learn about our Disclosure Policy.

