[ad_1]
Analytics company Canalys has released its latest report on China’s smartphone market for the first quarter of 2024, and Apple has come off worst among the top five brands jostling for supremacy in Asia’s largest economy.

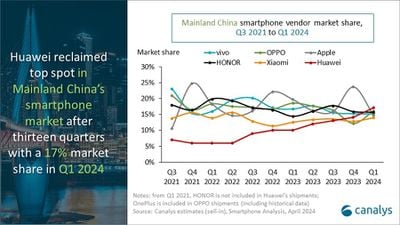
Huawei returned to the top spot after 13 quarters with a 17% market share. The local vendor shipped 11.7 million smartphones, thanks to its popular Mate and nova series, while OPPO rose to second place on strong performance of its Reno 11 series, shipping 10.9 million units. Conversely, HONOR, vivo, and Apple all slowed their sell-ins in the quarter, ranking third, fourth, and fifth, respectively.
HONOR shipped 10.6 million units with a 16% share, a year-on-year increase of 9%, while vivo shipped 10.3 million units with a 15% share, a year-on-year decrease of 9%. Apple declined the most among the top five, sinking to fifth from first place, with 10 million units and a 15% share, which is a year-on-year decrease of 25%.
Huawei’s performance is up 70% from a year earlier, when the company was still reorganizing its phone business following U.S. sanctions. Huawei’s 5G Mate 60 Pro uses a China-made 7-nanometer processor tailored for the local market, showcasing the kind of advanced semiconductor manufacturing capabilities that US sanctions were originally designed to prevent.
Huawei has since released its new Pure line of flagship smartphones, and has been busy developing its own operating system, HarmonyOS, since it could not use Google’s Android and Google Mobile Services. The continued expansion of the HarmonyOS ecosystem breaks the two-horse race of Android and iOS in Mainland China.

The latest data is unlikely to make for pleasant reading for Apple’s CEO Tim Cook, following his trip to China for the inauguration of a major new store in Shanghai. During his visit, coming on the back of a strong Chinese fourth quarter, Cook announced the expansion of Apple’s R&D center in the city, highlighting China’s crucial role in the company’s strategy. Cook also attended the China Development Forum in Beijing, where he said the country was “critical” to Apple.
Apple is deepening its ties with China despite expanding production in Southeast Asia and India. Approximately 17% of Apple’s net sales from October to December were derived from the greater China region, making it the largest regional supplier in the company’s supply chain. But Apple is facing an uphill battle to reverse falling iPhone sales there, with a 24% year-on-year decline in 2023 projected to deepen through 2024.
[ad_2]
Source Article Link

